For taxpayers who honestly pay their taxes, receiving an income tax notice can cause anxiety and tension. However, most notices are routine and easily manageable. Filing your ITR is essential, but in today’s data-driven tax ecosystem, it is not always the end of your tax journey.
The Income Tax Department now has extensive access to financial information through AIS/TIS, bank reports, and third-party data sources. This means receiving a notice does not always mean you’ve made a mistake — but it does require attention.
Some income tax notices simply inform you about an update or a mismatch, while others require additional documents or clarification. Before taking action, it is essential to verify the authenticity of the notice and understand why it was issued.
This guide explains everything you need to know — types of income tax notices, reasons for receiving them, documents required, and how to check whether your notice is genuine.
Key Takeaways
- An Income Tax Notice is an official communication from the Income Tax Department pointing out an issue or requesting clarification regarding your tax account.
- Common notices include: Section 133(6), Section 142(1), Intimation under Section 143(1), Scrutiny under Section 143(2), and Reassessment notice under Section 148.
- Depending on the case, a notice under Section 148 can be issued for up to 3, 10, or in special cases 16 years.
- Notices may be issued for mismatches, errors in ITR, incorrect income reporting, missing documents, pending tax, or high-value transactions not reported correctly.
- Failing to address a notice can lead to penalties, interest, and legal consequences.
Types of Income Tax Notices
An Income Tax Notice is a written communication issued by the Income Tax Department when clarification, correction, or additional information is required. Reasons include non-filing of returns, mismatched income, missing details, or discrepancies in reported information.
Not all notices indicate a serious issue — many are just requests for documents, explanations, or minor corrections.
Below are the major types of notices and how to respond effectively.
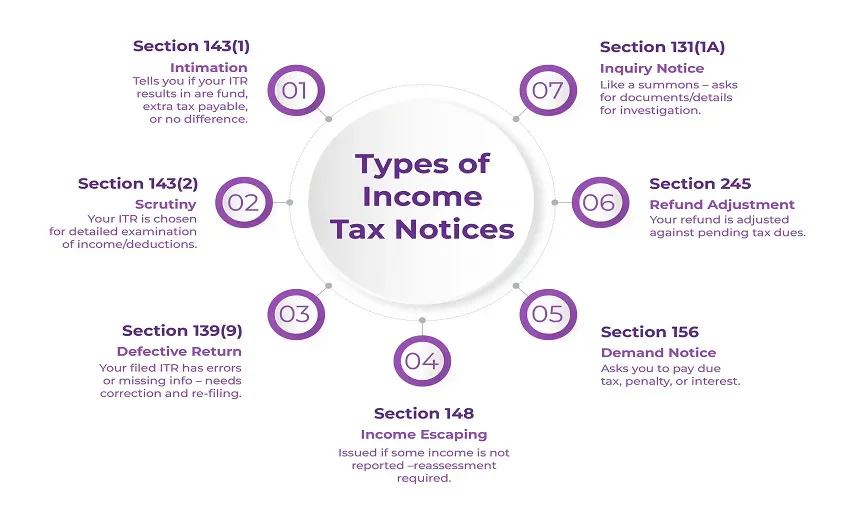
Notice Under Section 133(6)
Under Section 133(6), income tax officials can request additional information or documents if they find a discrepancy between the data available (AIS/TIS) and the ITR filed. This section is commonly triggered under the E-Verification Scheme 2021.
You may receive this notice if:
- Your income is above the basic exemption limit but ITR has not been filed.
- Income is taxable in the form of capital gains tax for NRIs, salary, and interest income, as stated in the Annual Information Statement (AIS). However, the amount is not correctly mentioned in the ITR form.
- You made high-value transactions like foreign travel, property purchase, investment in securities, but your income declared does not justify them.
How to Respond to Notice u/s 133(6)?
- Identify the reason for receiving the notice.
- Visit the Income Tax portal → Login → Pending Actions → Compliance Portal → E-Verification.
- Fill the form and upload supporting documents.
- If the mistake is from your side, file an updated return under Section 139(8A) and provide clarification.
- If the notice is due to an error by the department, respond using the Insights portal with proof.
Notice Under Section 142(1)
This notice is issued in two situations:
- You have filed your ITR but the officer needs more documents/information.
- You have not filed your ITR and the officer directs you to file it.
Consequences of Not Responding
- Penalty up to ₹10,000 for each failure (as per Section 272A).
- Prosecution up to one year.
- Further legal actions.
Intimation Under Section 143(1)
This is a summary of how the CPC processed your ITR. You may receive this intimation if there are:
- Incorrect claims or mismatched deductions
- Disallowance of expenses as per the audit report
- Arithmetical errors
- Incorrect tax, interest, or late fee calculation
You may receive the intimation under one of these outcomes:
- Refund due
- Demand payable
- No demand/no refund but change in loss amount
If there is a pending tax demand, it is vital to issue the intimation notice within nine months from the year-end in which the income tax return was filed. For instance, if you have filed your ITRs for the assessment year 2024-25 on July 27, 2024, then you can receive the intimation notice before 31 December 2025. From the accounting year 2017-18, it has been mandatory to process the ITR under this section.
How to Analyse the Intimation under Section 143(1) Notice?
- Compare the data computed under Section 143(1) with your ITR.
- Identify whether the variation is due to income, TDS, or deduction mismatch.
- If you disagree, file a rectification under Section 154 within 4 years.
Notice Under Section 143(2) (Scrutiny Notice)
This notice is issued when the income tax department finds errors or variations in the filed income tax return, whether big or small. It issues 143(2). The variations or errors in the ITR might involve over-reporting of financial losses or under-reporting of income. It is a notice for a detailed or scrutiny assessment. In simple terms, this notice indicates that the income tax officials have identified specific issues in your filed ITR, and they require your clarification. It is done to verify the reliability and correctness of several deductions stated by the taxpayer in his/her filed ITR. With detailed scrutiny, the tax officer wants to be sure that you have not made any of the following mistakes:
- Paid less tax than your liability
- Under-reported your income
- Over-claimed loss
After receiving this notice, you must answer the attached questionnaire with the required documents as specified by the income tax department. After the completion of the financial year to which it is associated, within three months, the income tax officer is supposed to provide you with this notice.
For Example
If Nishank filed his ITR on 20 May 2024 for AY 2024–25, he may receive a 143(2) notice on or before 30 June 2025.
How to Reply?
- Read the notice and review the annexure.
- Prepare a cover letter with explanations.
- Log in to Income Tax Portal → e-Proceedings.
- Upload your response with supporting documents.
Notice Under Section 148 (Reassessment)
Under section 148, the income tax department has the right to send a notice to the taxpayer if he/she deems that the income of the taxpayer in the filed ITR has not been properly assessed. In simple words, if the income tax officer has a valid reason to believe that the taxpayer has failed to mention some income in the ITR, he/she can send a notice to them under section 148.
Previously, the timeline to respond to the notice under section 148 was as follows:
According to the Finance Act 2021 amendment, which came into effect on 1 April 2021, the time limit within which the income tax officer can re-open the filed ITR of the taxpayer is as follows:
- In typical cases, up to three years from the end of the financial year
- Beyond three but not more than 10 years from the end of the relevant assessment year. If the tax officer has evidence that Rs 50 lakh or more in income for an accounting year has escaped assessment.
Time Limit to Issue Notice for ITR Filed Preceding to Finance Act 2021
These are the following time limit issues notice for ITR filed preceding the Finance Act 2021
- Up to 4 Years from the End of the Relevant Financial Year: A tax officer who is under the rank of Deputy Commissioner or Assistant Commissioner cannot issue the notice. Under section 148, a tax officer can only issue the ITR notice on the order of the Joint Commissioner after having valid reasons for doing so. For the financial year 2017-18, an ITR notice under Section 148 can only be issued until 31 March 2022 (here, the figures are assumed for the filed ITR preceding 2021, as per the Finance Act).
- Beyond 4 Years but up to 6 Years from the End of the Relevant Financial Year: Only the Chief Commissioner or Commissioner is authorised to issue this notice under section 148 if satisfied that income has escaped assessment. Here, the escaped income amount should be more than INR 100000. For the financial year 2017-18, this notice can be valid for issuance until 31 March 2024 (here, the figures are assumed for the filed ITR preceding the 2021 Finance Act).
- Beyond 4 Years but up to 16 Years from the End of the Relevant Financial Year: Under this provision, a notice can be issued if the income is related to an asset situated outside India that is taxable in India but has escaped assessment. The assets also include financial interests in any entity. For the financial year 2017-18, this notice is valid until 31 March 2034 (here, the figures are assumed for the filed ITR preceding the 2021 Finance Act).
Amendment Effect in Finance Act, 2021
According to the present provisions, you can issue the ITR notice up to four, six, or 16 years under Section 148, depending on the case. However, the new reassessment due dates, effective from 1 April 2021, were applicable. Confused? Through the given table, let us understand the timelines for previous accounting years after the Finance Act 2021 amendment came into force:
| Accounting Year in which income escapes assessment | Timeline Notice can be issued up to 3 years | Timeline if notice can be issued beyond 3 years but up to 10 years |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-21 | 31/03/2025 | 31/03/2032 |
| 2019-20 | 31/03/2024 | 31/03/2031 |
| 2018-19 | 31/03/2023 | 31/03/2030 |
| 2017-18 | 31/03/2022 | 31/03/2029 |
| 2016-17 | 31/03/2021 | 31/03/2028 |
| 2015-16 | - | 31/03/2027 |
Here, for the assessment year 2015-16, in typical cases, the tax officer cannot issue a notice under section 148. Additionally, for the accounting year 2016-17, the notice should be issued before 31 March 2021.
Notice Under Section 245
A notice under Section 245 is issued when the tax officer has a valid reason to believe that the previous year's tax has not been paid, and to balance it off, they want to adjust the amount by refunding the current year. Section 245 of the Income Tax Act, 1961, provides the Income Tax Department with the power to change the tax demand of the previous year by refunding the current year. However, to implement this power, the officer must send the notice under Section 245 of the IT Act, 1961, to the taxpayer and provide them with time to reply, whether they agree with it or not.
The timeline for responding to the notice is one month from the day the taxpayer receives it. If you fail to reply to the notice on time, the officer will consider this as your consent and proceed with the assessment. Therefore, please respond to the notice as soon as possible.
What to Do When You Receive the Income Tax Notice Under Section 245?
When you receive the income tax notice under section 245, you should consider taking the following steps:
- Step 1: Read the notice carefully and determine the reason for receiving it.
- Step 2: Verify the basic details of the notice to ensure it is intended for you or someone with the same name as yours. For this, please verify your name, PAN number, the mentioned address, and other details. Also, do not forget to check the financial year stated in the notice.
- Step 3: Verify the mismatch in your ITR that results in receiving this notice.
- Step 4: To avoid prosecutions and penalties, reply to the sent notice within the given timeline.
- Step 5: Ensure that you respond to the notice with sufficient information and a clear explanation.
- Step 6: Apart from this, check that the notice you received from the Income Tax Department is also shown on your online income tax account.
These are the different types of income tax notices that taxpayers often receive from the Income Tax Department under different sections. But have you ever considered the reasons behind receiving these notices? Want to know? Read the next section and get your answers.
Professional tax experts ready to resolve your notice and save you stress.
Most Common Reasons for Receiving an Income Tax Notice
The most common reasons for which you can get an income tax notice from the Income Tax Department under different sections are as follows:
- Mismatch between AIS/TDS and ITR
- Errors or omissions in reporting
- Wrong ITR form used
- High-value transactions not declared
- Unreported capital gains
- Pending self-assessment tax
- Incorrect reporting of spouse-related investments
- Late filing
- Refund adjustment cases
- General scrutiny
Things to Do After Getting a Notice from the Income Tax Office
Under any of the above-mentioned income tax sections, if you received an ITR notice, you should follow these steps:
- Read the notice carefully to identify the reason.
- Verify your personal details (PAN, name, address, mobile).
- Check the assessment year and mismatch details.
- Respond within the stipulated timeline.
- Attach valid supporting documents.
- Check whether the notice appears in your e-Filing account.
Consequences of Ignoring a Notice
- Penalties and fines
- Additional tax liability
- Loss of exemptions
- Interest under Sections 234A/B/C
- ITR may be treated as invalid
- Damage to tax history or financial profile
Documents Required to Answer an Income Tax Notice
The documents you need to submit in reply to the notice you received from the Income Tax Department depend on the type of notice. However, some of the papers remain common in all income tax notices. These are as follows:
- Copy of the notice
- Form 16 / Salary Slips
- Income proofs (bank interest, capital gains reports)
- Investment proofs
- TDS certificates (including Section 195 for NRIs)
How to Authenticate an Income Tax Notice?
Before you reply to any notice received in the name of the Income Tax Department, it is essential to verify whether it is genuine or not, or is issued by the Income Tax officials. Here is how you can check the authenticity of the received notice:
- Step 1: Visit the online income tax portal and, using your credentials, log in to your account. Under the "Quick Links" section, click on "Authenticate Order/notice issued by the ITD."
- Step 2: Using your financial year, mobile number, PAN card, document type, and issue date, you can verify your income tax notice. You can also use your Document Identification Number (DIN) and mobile number to authenticate the notice you received from ITR.
- Step 3: To authenticate the notice using the financial year, PAN number, date of issue, and mobile number, choose the correct option and mention the requested information.
- Step 4: Once you have mentioned all the details, you will receive an OTP on your registered mobile number. Enter the received OTP. After its validation, you will see your DIN and the issue date of the notice on the screen. In case of your name, no notice is issued by the income tax department; a message will be shown on your screen stating, "No details found for the given criteria."
- Step 5: Another way to check the authentication of your ITR notice is by using your mobile and DIN number.
- Step 6: Enter your mobile number and DIN number, and proceed with the process. You will receive an OTP on your registered mobile number. Validate the information using OTP. If the income tax department has issued an order or notice, a success message will be displayed on your screen, stating, "Yes, notice/order issued by the income tax authority for the details entered." If you did not receive a message from the authority, the screen will display, "No record found for the given DIN number."
Final Thoughts
This article is about the income tax notice and how to check and authenticate it online. The taxation system of India is no longer passive. It is now proactive, AI-driven, and automated. For Indian residents, entities, and NRIs, the best way to avoid receiving a notice from the Income Tax Department is to maintain transparency and respond in a timely manner. Disclose your income, match your information, file returns, and properly submit your documents. You are not just filing taxes; you are also protecting your financial standing. With this, if you need more information on the income tax notice, DTAA agreement or need assistance in replying to the notice, connect with Savetaxs. We have a team of professionals with years of expertise in national and international tax assignments, and we can assist you with your tax notice. So, why take stress when you have the option to get guidance? Contact us today and solve all your doubts.
Note: This guide is for information purposes only. The views expressed in this guide are personal and do not constitute the views of Savetaxs. Savetaxs or the author will not be responsible for any direct or indirect loss incurred by the reader for taking any decision based on the information or the contents. It is advisable to consult either a CA, CS, CPA or a professional tax expert from the Savetaxs team, as they are familiar with the current regulations and help you make accurate decisions and maintain accuracy throughout the whole process.
Speak to our experts and get personalized solutions for your NRI tax needs
View Plan- NRI Income Tax in India (2025): Rules, Slabs, Capital Gains & ITR Forms
- ITR 2 for NRIS: All You Need to Know for FY 2024-25
- What Is Form 16: A Comprehensive Guide
- Income Tax Act Section 148: Assessment or Reassessment
- Understanding All About Income Tax Clearance Certificate
- Section 147 of the Income-tax Act, 1961 (ITA) Demystified
- Section 144B Of Income Tax Act: Faceless Assessment Scheme
- What is ITR 3 and How Can an NRI File It Online?
- Section 144 of the Income Tax Act: Best Judgement Assessment
- PAN Card for NRIs - Comprehensive Guide
- What is the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Singapore?
- Everything You Need to Know About Form 15CA and 15CB of Income Tax
- TDS on Sale of Property by NRIs in India
- NRE & NRO Accounts - Meaning, Comparison, Benefits, Taxation
- TDS Certificate Form 16A For NRIs: TDS on Indian Income
- Section 54F of Income Tax Act - Exemption on Purchase of Residential Property
- Form 61A Income Tax: Applicability, Due Date & How to File SFT Online

Mr. Ritesh has 20 years of experience in taxation, accounting, business planning, organizational structuring, international trade financing, acquisitions, legal and secretarial services, MIS development, and a host of other areas. Mr Jain is a powerhouse of all things taxation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Have you received an Income Tax notice as an NRI? Get straightforward answers on what it means, why you received it and how to respond to it quickly and correctly.
In terms of income tax, intimation is merely the outcome of ITR processing, and in this case, an individual does not need to take any further action. However, when you receive a notice from the Income Tax Department, it requires further action along with proper clarification of the requested information.
A tax notice number is a computer-generated, 20-digit, unique number. For every conversation, including notices, letters, orders, and other correspondence, this number is mandatory and is issued by the income tax official to include the quoted documentation identification number (DIN).
According to the current rules and guidelines of the Income Tax Act 1961, any person/ business, irrespective of the income earned, is liable to file an ITR in India. However, currently, a person or business whose income exceeds Rs. 2.5 lakh in an assessment year is liable to pay tax in India.
A tax roll notice is associated with the notice related to property tax within a stated jurisdiction. These notices are generally maintained by the municipal department of the government to which taxes of property taxes are owed. Additionally, according to the type of assets, the tax roll notices are maintained by a different department, such as the motor vehicle department, or more.
In case you do not respond to the Income Tax notice on time, your filed income tax return will be considered invalid. Additionally, you need to pay high penalties and interest on the ITR.
Generally, the refund process takes 20-45 working days once the e-verification is done by the Income Tax return. In case you send the acknowledgment physically, the CPC may take longer to process your refund.