Every person wants to earn as much money as possible, and because of this, they always look for investment options and ideas that can grow their wealth in India as well as overseas. Also, many individuals reside in one country but earn money in another. But do you know that on investment returns and the money they generate outside their residential country, they may need to pay tax?
However, paying double tax on the same income in different countries is no doubt unfair for an individual. This problem is generally faced by NRIs. Considering this, the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) for NRIs comes to the rescue. So, if you are an NRI facing the problem of double taxation and want to know how to avoid it, then this guide is for you. Let’s begin.
Key Takeaways
- A Double Tax Avoidance Agreement is a contract signed between India and other countries, under which a person can avoid paying tax on the same income twice.
- India has signed the DTAA agreement with over 85 countries.
- This tax treaty avoids double taxation, promotes investment and international trade, and prevents tax evasion.
- It applies when a company or an individual is required to pay taxes on the same income in two different nations.
- The DTAA rates, validity periods, and rules and regulations may vary by country.
- You can categorize tax relief under DTAA into two types: bilateral and unilateral tax reliefs.
- An NRI needs to submit Form 10F, a Tax Residency Certificate (TRC), and a PAN card number to claim DTAA benefits.
What Is a Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)?
Do you know that India has signed DTAA agreements with over 85 countries? A Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) is a contract signed between India and other countries. As per this agreement, a person who is a resident of one country but earns income in another does not need to pay tax twice on the same income.
For instance, suppose you are an NRI earning a salary income in the UK by working for a UK company. As per general tax laws, your income may be taxable in both countries—India (as a resident country, if applicable) and the UK (as a source country). However, through the DTAA agreement, you can avoid paying taxes twice on the same income. You either pay tax in only one country or receive a tax credit for the tax paid abroad.
Objectives of DTAA
The key objective of the DTAA agreement is to ensure that no individual pays taxes twice on the same income in two different countries. Apart from this, some of the objectives of the DTAA agreement are:
- Avoid Double Taxation: Ensure that taxpayers do not pay tax twice on the same income, reducing the burden on international income.
- Promote Investment and International Trade: By decreasing tax burdens and providing clear tax rules, DTAA encourages cross-border economic activities.
- Tax Relief: Provide tax exemptions, tax credits, and reduced tax rates to prevent double taxation.
- Preventing Tax Evasion: The agreement allows for the exchange of information between countries to prevent fraud and tax evasion.
- Certainty and Clarity: Offer clear rules on taxable income to simplify tax administration and reduce disputes.
An Illustration
Arjun, a resident of India, earns ₹2,500 through his investments in the UK. This income is taxable in both India and the UK. Let’s assume the tax rate in each country is 30%. Without DTAA, Arjun would end up paying 60% tax (30% + 30%), leaving him with only ₹1,000 after tax.
This dual taxation situation is a loss for Arjun. To avoid this, the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement comes to the rescue. Under DTAA provisions, foreign income can be taxed once, either in any one country or with credit for tax paid in the other. This ensures individuals are not overburdened with double taxation.
When a person knows that they will not be taxed twice on their global income, it motivates them to expand their earning potential internationally. It also helps countries attract global investments. Through this, India benefits from foreign investments, and foreign countries benefit from Indian entrepreneurs. Hence, the DTAA agreement is beneficial for all participating countries and helps promote economic growth.
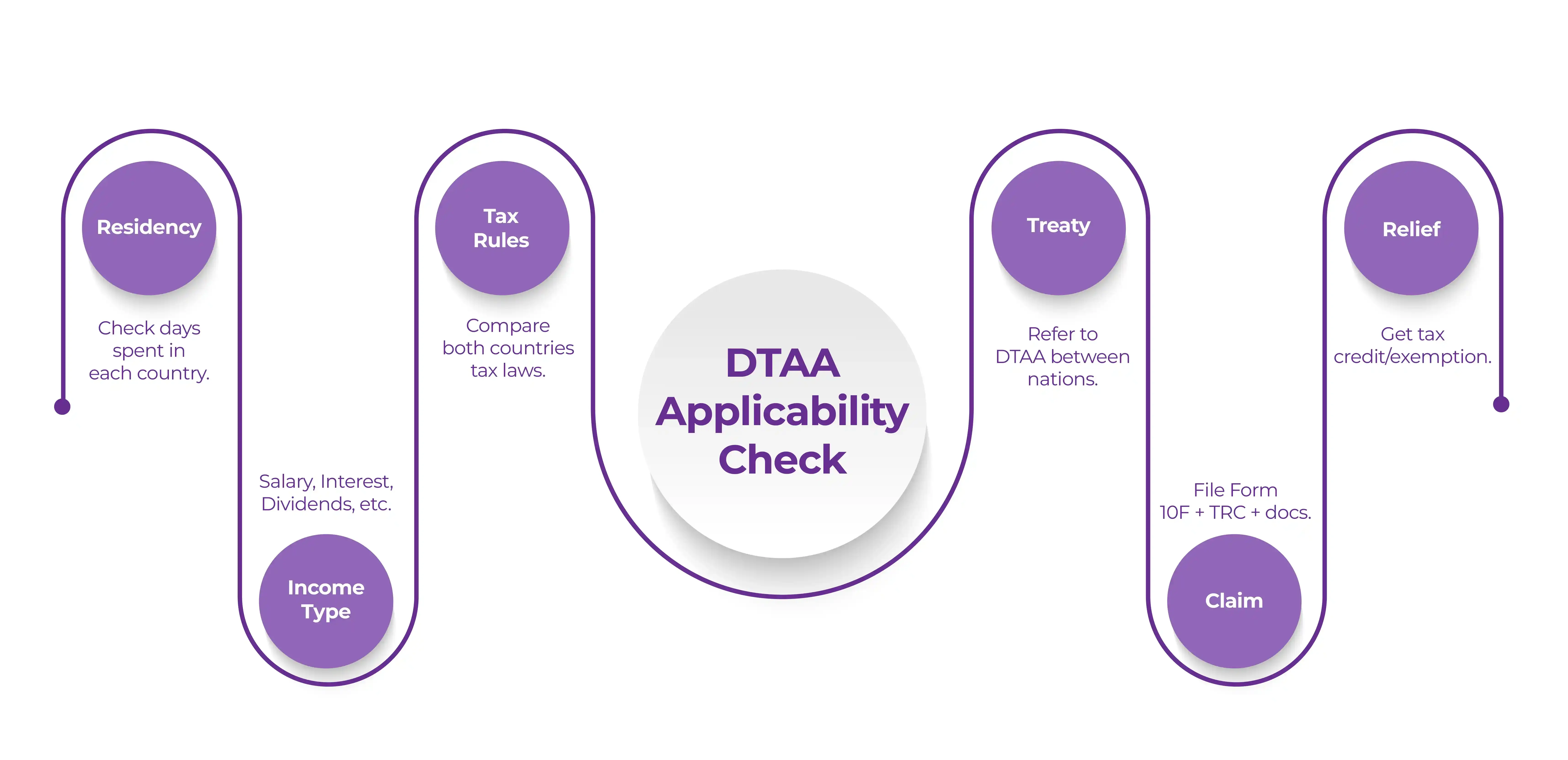
How to Determine Whether DTAA Is Applicable or Not?
The DTAA agreement is applicable when a company or an individual may be taxed on the same income in two different countries. Here’s how to determine its applicability:
- Residency Status: Determine the residential status of the individual based on the tax laws of each country.
- Nature of Income: Identify whether the income is salary, interest, dividends, etc., and whether it is taxable in both countries.
- Tax Rules in Each Country: Understand the applicable tax rules and rates.
- Applicable DTAA: Review the DTAA between the two countries to know which country has the primary taxing right.
- Claiming Benefits: If DTAA benefits apply, follow the correct procedure like submitting forms and documents.
- Avoidance of Double Taxation: DTAA provides mechanisms like reduced tax rates, exemptions, and tax credits.
Benefits of DTAA
Signing a Double Tax Avoidance Agreement comes with several advantages:
- Makes a country an attractive destination for foreign investment and business.
- Prevents tax evasion by offering relief from paying tax twice on the same income.
- Tax relief is provided through complete avoidance or tax credit.
- Offers concessional tax rates.
- Lower withholding tax helps taxpayers pay reduced TDS on income such as interest, royalty, and dividends.
Documents Required for Claiming DTAA Benefits
Initially, before claiming DTAA benefits, you should check the DTAA income tax agreement between your residential country and the other foreign country where you are planning to go. Once you go through it, you need to submit several documents for tax exemption or claim a tax credit. Do you know that to claim the DTAA benefits, NRIs need to submit several documents? Want to know what they are? Here is the list of the following documents required for claiming DTAA benefits.
Here is the list of documents:
- Indemnity form or Self-Declaration form
- Self-attested valid visa (where applicable)
- Photocopy of PIO proof (if applicable)
- Self-attested photocopy of PAN card
- Tax Residency Certificate (TRC)
- Self-attested copy of passport
Additionally, to claim tax benefits under the DTAA agreement, NRIs must provide a Tax Residency Certificate (TRC) to the deductor. As per Sections 90 and 90A of the Income Tax Act, to obtain your TRC from India, you need to submit Form 10FA. After verification, the TRC is issued.
NRIs must also provide Form 10F, which contains details required to treat the individual as a resident of another country for DTAA purposes.
What Are the Different DTAA Rates for Various Countries?
DTAA rates are not the same for every country - they depend on the mutual agreement between both nations. Also, these agreements do not have a fixed validity period; they continue until one nation terminates the contract.
Rules and regulations under DTAA may change based on decisions taken by the contracting states. Typically, on interest income, TDS rates range between 10% and 15%.
Under Section 195 of the Income Tax Act, dividend income paid to foreign or non-resident companies is chargeable based on the applicable DTAA rates. These concessional rates help attract foreign investment and provide tax relief to residents.
India has signed DTAA contracts with over 85 countries, such as the USA, UK, UAE, Canada, Australia, Singapore, and many more (full list can be added as needed).
| Sr. No. | Country | TDS Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Armenia | 10% |
| 2. | Australia | 15% |
| 3. | Austria | 10% |
| 4. | Bangladesh | 10% |
| 5. | Belarus | 10% |
| 6. | Belgium | 15% |
| 7. | Botswana | 10% |
| 8. | Brazil | 15% |
| 9. | Bulgaria | 15% |
| 10. | Canada | 15% |
| 11. | China | 15% |
| 12. | Cyprus | 10% |
| 13. | Czech Republic | 10% |
| 14. | Denmark | 15% |
| 15. | Egypt | 10% |
| 16. | Estonia | 10% |
| 17. | Ethiopia | 10% |
| 18. | Finland | 10% |
| 19. | France | 10% |
| 20. | Georgia | 10% |
| 21. | Germany | 10% |
| 22. | Greece | According to the agreement |
| 23. | Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan | 10% |
| 24. | Hungary | 10% |
| 25. | Iceland | 10% |
| 26. | Indonesia | 10% |
| 27. | Ireland | 10% |
| 28. | Israel | 10% |
| 29. | Italy | 15% |
| 30. | Japan | 10% |
| 31. | Kazakhstan | 10% |
| 32. | Kenya | 15% |
| 33. | South Korea | 15% |
| 34. | Kuwait | 10% |
| 35. | Kyrgyz Republic | 10% |
| 36. | Libya | According to the agreement |
| 37. | Lithuania | 10% |
| 38. | Luxembourg | 10% |
| 39. | Malaysia | 10% |
| 40. | Malta | 10% |
| 41. | Mauritius | 7.50-10% |
| 42. | Mongolia | 15% |
| 43. | Montenegro | 10% |
| 44. | Morocco | 10% |
| 45. | Mozambique | 10% |
| 46. | Myanmar | 10% |
| 47. | Namibia | 10% |
| 48. | Nepal | 15% |
| 49. | Netherlands | 10% |
| 50. | New Zealand | 10% |
| 51. | Norway | 15% |
| 52. | Oman | 10% |
| 53. | Philippines | 15% |
| 54. | Poland | 15% |
| 55. | Portuguese Republic | 10% |
| 56. | Qatar | 10% |
| 57. | Romania | 15% |
| 58. | Russia | 10% |
| 59. | Saudi Arabia | 10% |
| 60. | Serbia | 10% |
| 61. | Singapore | 15% |
| 62. | Slovenia | 10% |
| 63. | South Africa | 10% |
| 64. | Spain | 15% |
| 65. | Sri Lanka | 10% |
| 66. | Sudan | 10% |
| 67. | Sweden | 10% |
| 68. | Swiss Confederation | 10% |
| 69. | Syrian Arab Republic | 7.50% |
| 70. | Tajikistan | 10% |
| 71. | Tanzania | 12.50% |
| 72. | Thailand | 25% |
| 73. | Trinidad and Tobago | 10% |
| 74. | Turkey | 15% |
| 75. | Turkmenistan | 10% |
| 76. | UAE | 12.50% |
| 77. | UAR (Egypt) | 10% |
| 78. | Uganda | 10% |
| 79. | UK | 15% |
| 80. | Ukraine | 10% |
| 81. | United Mexican States | 10% |
| 82. | USA | 15% |
| 83. | Uzbekistan | 15% |
| 84. | Vietnam | 10% |
| 85. | Zambia | 10% |
Application of DTAA
The DTAA agreement can be applied either in a limited manner or comprehensively. Let’s understand both types:
Limited DTAA
Under a limited DTAA, tax relief is available only for specific income categories such as:
- Income from air transport
- Income from shipping
- Income from gifts
- Income from inheritance
- Income from the estate
Comprehensive DTAA
Under a comprehensive DTAA, tax benefits apply to a wider range of income categories, including:
- Income from capital gains (long-term or short-term)
- Other taxable income sources
Income Exempted Under DTAA for NRIs
Based on the DTAA provisions between India and respective countries, NRIs do not need to pay tax twice on the following income earned in India:
- Salary received
- Interest earned on fixed deposits in India
- Salary earned for services rendered in India
- Capital gains earned from transfer of assets in India
- Interest earned on savings bank accounts in India
- Income from house property situated in India
How Does the DTAA Agreement Work?
DTAA works on two main principles:
- Source Rule: You pay tax in the country where the income originates, regardless of your residency.
- Resident Rule: You pay tax in the country where you live, even if the income is earned abroad.
India follows the residence rule.
- If you receive foreign income and are a resident of India, you must pay tax in India.
- If you are an NRI and earn income in India, the income is taxable in India and may also be taxed in your country of residence.
However, instead of paying tax twice, you can claim DTAA benefits.
What Tax Reliefs Come Under DTAA as per Indian Tax Laws?
Tax reliefs under DTAA can be divided into:
1. Bilateral Relief – Section 90 (Income Tax Act, 1961)
These tax reliefs are applicable in those countries with which India has signed the DTAA agreement. At present, India has signed this agreement with 80+ countries. Under the bilateral relief, you can claim the tax benefits in two ways. These are as follows:
- Exemption Method: In this, the income you earn globally is taxed in one country, or a specific part of it is taxed in both countries, i.e., from where it originated and your resident country.
- Tax Credit Method: In the tax credit method, the income you earn is taxed in both countries. After you pay the tax on your income from where it originated, you get a tax credit on the liable tax amount in your resident country. For example, if you earned money in the USA and paid the tax there, after that, when your tax liability is calculated in India (resident country) on your total earned income, the tax amount you already paid in the USA will be deducted.
Also, the DTAA agreement overrules the Income Tax provisions. This means that you can choose any of the provisions that are more favourable to you.
2. Unilateral Relief – Section 91 (Income Tax Act, 1961)
If there is no DTAA agreement signed between India and the country from which you are earning, you get unilateral tax relief. To avail of the unilateral benefits, you need to fulfil the following conditions:
- In the year you earned your income, you should be a resident Indian.
- The income you earn should be from outside India.
- It should be taxable in a foreign country, and you should pay that tax.
Under this method, you would pay the tax twice, and the Indian income tax will also be applicable. The tax deduction rate will be less than the average tax rate of India or the country from which you originated your foreign income, whichever is less. The average tax rate will be calculated by dividing the paid tax by the total earned income, multiplied by 100. If both taxes are equal, the Indian tax rate will be deducted.
Plan smarter with our DTAA calculator. Find out how much tax you can save under treaty rules.
How Can NRIs Claim DTAA Benefits?
To avail of the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) benefits, NRIs living in a DTAA country need to submit the following documents:
- Form 10F: To avail of the benefits under the DTAA agreement, NRIs need to fill out the Form 10F. It is one of the essential documents when applying for DTAA.
- Tax Residency Certificate (TRC): If you want to get tax benefits under DTAA, you need to have a Tax Residency Certificate (TRC) by your side. It is one of the mandatory documents required during the application process. To get a TRC certificate, you can apply from the government website of the country where you currently reside.
- PAN Card Number: You also need to provide your PAN card number along with the above-stated documents.
Example: DTAA Tax Calculation
For example, consider B, an NRI resident of country R who earns income from country N.
- Tax rate in country R = 30%
- Tax rate in country N = 50%
| Particulars | Exemption Method | Deduction Method | Tax Credit Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foreign Income | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Foreign Income Tax (30%) | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Net Domestic Income | 70 | 100 | Nil |
| Domestic Tax | 35 | 50 | Nil |
| Credit | - | (30) | - |
| Final Domestic Tax | 35 | 20 | Nil |
| Total Domestic and Foreign Taxes | 65 | 50 | 30 |
How to Apply for a DTAA Agreement?
There are three ways by which you can claim the DTAA benefits:
- Exemption: This can be claimed in only one country, either the country where you earned income or your residence country, subject to specific conditions.
- Tax Credit: You can claim credit on your paid tax in the country where you currently reside.
- Deductions: The residence country allows the taxpayers to claim a deduction on the paid tax in a foreign country on the same income.
For instance, Mr. D is a resident of India, but his income originates from the UK. Now, here is the income you earn from the UK that is taxable in both countries, India and the UK. Under the DTAA agreement, Mr. D can claim tax relief and pay the tax in only one country. Usually, the taxpayers are either granted a deduction, tax credit, or exemption in the resident country.
Services Exempted Under DTAA Agreement
The income originated from the following sources, exempt under the DTAA agreement, is as follows:
- House property situated in India
- Savings account in India
- Services provided in India
- Fixed deposits in India
- Capital gains received from asset transfer in India
- Salary received in India
Pre-conditions for Tax Relief (DTAA Not Present or Not Used)
Double taxation happens when you pay taxes on the same income twice in two different countries. It creates a significant tax burden on the companies and individuals that have foreign income sources, with Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs) with 94 countries. These agreements provide clarity to the taxpayers and allow them to claim tax relief on taxes that they paid overseas against their tax liability in India on the same income. It is mentioned in Section 90 of the Income Tax Act, certifying fair treatment for global income earners.
In case India does not sign the DTAA agreement with a specific nation or if you opt not to use the agreement, Section 91 of the Income Tax Act provides an effective solution through unilateral tax relief. Only under certain conditions can you claim this tax relief:
- Earned Income: The income should be earned in the last accounting year.
- Comparable Tax System: The tax system of the foreign country should be comparable to India. In addition to this, India has not signed the DTAA agreement with this country.
- Tax Liability: The earned income should be taxed in both countries, i.e., where it originated and where it is received.
- Tax Payment: The taxpayer needs to pay tax in the foreign country.
- Tax Relief Calculation: The unilateral tax relief amount should be less than the tax rate of India and the foreign country on the foreign income. This unilateral tax relief amount is then subtracted from the overall Indian tax liability of the taxpayer.
To claim unilateral tax relief under Section 91 or bilateral tax relief under a DTAA agreement, an NRI needs to file an Indian income tax return (ITR) and provide a tax deduction or payment certificate from the official foreign tax authority.
Final Thoughts
This was your complete guide for the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) for NRIs. With this agreement, not only NRIs but any individual who earns income globally can avoid paying the tax twice on the same income. However, the double taxation rule may vary depending on the country. Considering this, it is advisable to check the rules and regulations of both countries before filing the DTAA petition. Furthermore, if you need more guidance and information about the DTAA for NRIs, connect with Savetaxs. We are a team of tax experts who can help you in solving any tax-related query. Additionally, can also assist you in filing your ITR and getting DTAA benefits.
Speak to our experts and get personalized solutions for your NRI tax needs
View Plan- What is the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Singapore?
- New NRI Taxation and Residency Rules Under the Income Tax Act
- What is Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)? How NRIs can Claim Benefits Under DTAA
- Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and UK
- Sections 90, 90A & 91 of the Income Tax Act for NRIs
- Form 10F: Purpose, Applicability, Requirements, How to Download and Fill Form 10F Online
- NRI Capital Gains and Their Taxability in India
- NRI Income Tax in India (2025): Rules, Slabs, Capital Gains & ITR Forms
- What are the NRI Tax Slab and Rates for FY 2024-2025 For NRIs?
- A Comprehensive Guide on the DTAA between India and the USA?
- What is the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Singapore?
- Everything You Need to Know About Form 15CA and 15CB of Income Tax
- TDS on Sale of Property by NRIs in India
- NRE & NRO Accounts - Meaning, Comparison, Benefits, Taxation
- TDS Certificate Form 16A For NRIs: TDS on Indian Income
- Section 54F of Income Tax Act - Exemption on Purchase of Residential Property
- Form 61A Income Tax: Applicability, Due Date & How to File SFT Online

Mr Shaw brings 8 years of experience in auditing and taxation. He has a deep understanding of disciplinary regulations and delivers comprehensive auditing services to businesses and individuals. From financial auditing to tax planning, risk assessment, and financial reporting. Mr Shaw's expertise is impeccable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Answers to your DTAA questions - Clear guidance for NRIs to claim tax relief correctly.
A DTAA agreement is a contract signed by two countries to prevent businesses and individuals from paying taxes on foreign-earned income twice and boost economic activities by attracting investors. The DTAA agreement helps NRIs in getting tax relief by providing a Tax Residency Certificate to their tenant. It significantly reduces the rate of TDS based on the DTAA contract terms.
Under the Income Tax Act 1961, Sections 90 and 91 offer specific tax reliefs to the taxpayers and help them avoid paying taxes twice. Section 90 helps with provisions including taxpayers who paid tax to a foreign country with which India has signed a DTAA, and section 91 deals with those nations that do not have any DTAA agreement with India.
NRIs can claim the DTAA benefits by submitting the Tax Residency Certificate or TRC to a deductor. To get the certificate, they need to fill out Form 10FA. It is available on the Income Tax website of India online.
India has signed the DTAA agreement with 88 foreign countries, out of which 86 are in force currently. In this, the countries have agreed on tax rates and jurisdiction on specified income types transactions, including individuals having income between countries with which India has signed the DTAA agreement.
Incomes that are covered under DTAA for NRIs include income from business profits, interest, capital gains, employment, dividends, and royalties. These agreements specify regulations as to which nation holds the right to impose taxes on a specific income type.
You can claim tax credit under the DTAA agreement if you belong to a country with which India has signed this agreement. For this, you need to fill out the ITR form and submit the required documents.