- What Is a Tax Residency Certificate (TRC)?
- Types of Residential Status Under Income Tax
- Key Benefits of a Tax Residency Certificate
- Eligibility Requirements for Obtaining a TRC
- How to Apply for a Tax Residency Certificate in India?
- Understanding Form 10F and Why It Is Required
- Step-by-Step Guide to Obtain a Tax Residency Certificate for NRIs
- Final Thoughts
In today's world, many individuals and businesses earn income from more than one country. With the increase in overseas investments and cross-border transactions, handling the tax obligations has become difficult. In this, one key tool helping in handling this complexity is the Tax Residency Certificate (TRC).
It is a document that plays a key role in avoiding paying tax on the same income twice through the provisions of Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA). Further, to obtain a TRC, you need to connect with the tax officials of the country where you are currently tax resident.
Want to know more about TRC? This blog provides you with all the information related to the tax residency certificate, its benefits, eligibility criteria, and how to apply for it. So, read on and gather all the details.
- TRC serves as proof of tax residency of individuals or entities and helps them to claim tax benefits under DTAA.
- TRC is a vital document issued by the income tax department of the resident country of the taxpayer. For several countries, like India, it is the basis of taxation.
- TRC also helps in getting tax treaty benefits, like lowering the rates of withholding tax on certain income types. It includes interest, royalties, dividends, and more. Additionally, it also simplifies the cross-border transaction while staying compliant with the global tax laws.
- The process of obtaining the TRC varies from country to country. Generally, to get the certificate, you need to submit documents like income details, tax identification number, residency proof, etc., to the tax officials.
- Form 10F is a self-declaration form filled by NRIs in the absence of certain information on their TRCs.
What Is a Tax Residency Certificate (TRC)?
A tax residency certificate (TRC) is an official document that is issued by the income tax department of the resident country of the taxpayer to prove that the individual in that particular financial year was a tax resident of that country.
Considering this, in India, people who qualify as "Resident and Ordinarily Resident (ROR) are liable to pay tax on their global income in India. Additionally, Non-resident taxpayers are also liable to pay tax in India on the income they earn in the country. Further, the income of the taxpayer is also taxable in the foreign country from where it originated, leading to double taxation.
To avoid these types of circumstances, India, with around 100 countries, has signed a double taxation avoidance agreement. However, to get the DTAA benefits, taxpayers need to provide a TRC certificate to prove that India is their resident country. NRIs can also claim tax benefits under DTAA by obtaining a TRC from their current resident country.
Furthermore, in the tax residency certificate, the following income types are covered:
- Income from overseas services.
- Earning from assets located in foreign countries.
- Salary income in foreign countries.
- Income generated from shares and mutual fund dividends earned overseas.
- Interest earnings from fixed deposits and savings accounts in foreign countries.
- Capital gains earned from transferring property in foreign countries.
- Revenue earned from the sale of agricultural products.
Apart from this, this certificate remains valid from the issue date until the end of the financial year. Considering this, taxpayers must apply for the DTAA benefits every year to gain them.
So, this was all about TRC. Moving ahead, let's know the types of residential status under the Income Tax Act 1961.
Types of Residential Status Under Income Tax
To obtain a TRC, under the Income Tax Act, 1961, you should qualify as an Indian tax resident. Considering this, in India, there are three types of residential status. These are as follows:
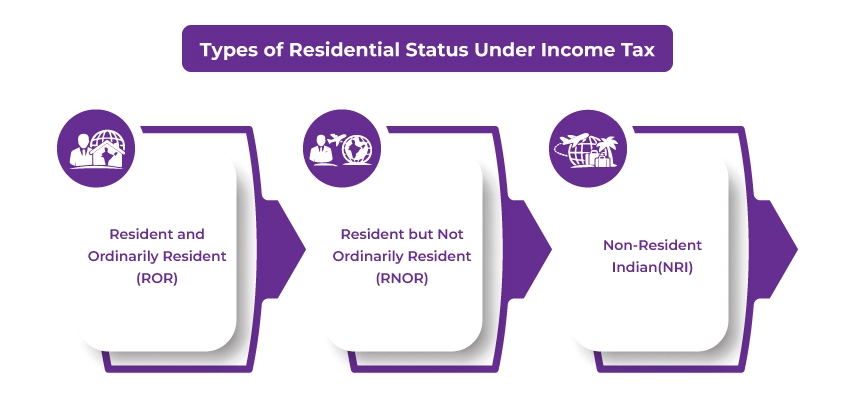
Resident and Ordinarily Resident (ROR)
According to Section 6(1) of the Income Tax Act, individuals are considered deemed residents if they fulfill the following criteria:
- Within a fiscal year, they live in India for 182 days or more.
- Within a time period of 7 years before the present financial year, they stay in India for 730 or more days.
- If, within 4 years preceding the previous year, they live in India for 356 days or more and come under the category of ordinary resident.
However, this criterion has changed. Now, as per section 6(6), to come under the resident and ordinarily resident category, they need to fulfill the following criteria:
- In the last 10 financial years preceding the present year, if they have resided in India for at least 2 years.
- Further, in the last 7 years preceding the present financial year, you have resided in India for 730 days or more.
Resident but Not Ordinarily Resident (RNOR)
To be categorized as a Resident but Not Ordinarily Resident, you need to fulfill the following criteria:
- In the last fiscal year, if you stayed in India for 730 days or more.
- In the previous financial year, if you resided in India for at least 2 out of 10 days.
Non-Resident Indian (NRI)
To be categorized as a non-resident Indian, you need to fulfill the following requirements:
- Within a financial year, if you stayed in India for less than 182 days.
- Within a fiscal year, if you live in India for not longer than 60 days.
- In the last four financial years, if you reside in India for more than 60 days but less than 365 days.
These were the different types of residential status as per the Income Tax laws. Moving further, now let's look at the key benefits of a tax residency certificate.
File your Income tax returns and stay compliant with the tax regulations.
Key Benefits of a Tax Residency Certificate
In several ways, for both individuals and businesses, a TRC is beneficial, specifically for those who are engaged in cross-border investments and transactions. Further, to provide you with an idea, here are some key perks of obtaining a TRC:
Avoidance of Double Taxation
The key purpose of a TRC is to help individuals avoid paying double taxes on the same income. This certificate helps you claim the tax benefits under DTAA. It validates the tax residency status of the individual, certifying that they do not pay tax on the same income twice.
Proof of Tax Residency for Financial Transactions
A tax residency certificate also serves as residency proof for conducting financial transactions. It includes opening bank accounts, making investments, and participating in international trade. Considering this, many foreign countries ask for the TRC to check the residential status of a person. This further increases the credibility and transparency in global transactions, helping in smooth financial transactions.
Eligibility for DTAA Benefits
For individuals and businesses, specifically for NRIs, TRC helps comply with the global tax laws. It serves as a basis for filing tax returns in both countries, i.e., resident and income source countries. Additionally, help in claiming the tax benefits that come with DTAA treaties. This includes a lower rate of withholding tax on specific income types like interest, dividends, royalties, and more.
Essential Document for Tax Compliance
When it comes to complying with international tax laws, TRC serves as a vital document. This certificate helps in identifying the tax residency status of the assessee. It is important when filing tax returns, dealing with tax officials, or financial institutions.
Simplifies Cross-Border Tax Procedures
Multinational businesses need to have a TRC. It helps in easing the tax-related administrative process, certifying that the correct tax treatment is received by them. Additionally, it also minimizes the chances of having disputes with the foreign tax officials.
These were some of the key benefits offered by tax residency certificates to individuals and businesses. Moving ahead, now let's know the eligibility requirements for obtaining a TRC.
Eligibility Requirements for Obtaining a TRC
To obtain a tax residency certificate, you need to meet the specific eligibility criteria. Considering this, the requirements are as follows:
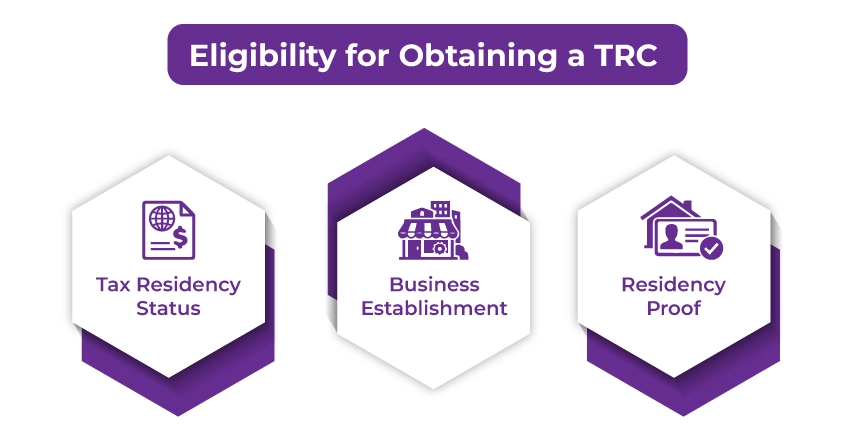
- Tax Residency Status: You need to be classified as a tax resident of the country that is issuing the TRC.
- Business Establishment: If applying TRC as a business entity, you should have a fixed business place in a foreign country.
- Residency Proof: In case you are applying for a TRC in a foreign country, you need to provide your foreign residential proof, such as a domicile certificate.
So, this was all about the eligibility requirements for obtaining a TRC. Moving further, let's know how you can apply for this certificate in India.
How to Apply for a Tax Residency Certificate in India?
To obtain a tax residency certificate in India, you can apply for it through the Income Tax Department. To claim a TRC, you need to fill out Form 10FA and submit it to the assessing officer.
Further, if the assessing officer is satisfied with your application, via Form 10FB, they will issue you a TRC. This form contains information about your tax residential status for that specific financial year. Additionally, helps you to claim the tax benefits under the DTAA regulations.
This is how you can simply apply for TRC in India: by visiting the Income Tax Department and filling out the application form. Moving ahead, let's know what Form 10F is and when it is needed.
Understanding Form 10F and Why It Is Required
Form 10F, in simple words, serves as an identification proof to confirm whether the assesses have paid taxes in their resident country or not. It consists of the time period for which the individual has been a resident of that country. Further, it mentions all these details in the TRC when it is issued.
Considering this, if the foreign TRC does not have vital information needed by the Indian tax officials, NRIs need to fill out this form. It includes nationality, overseas address, and Tax Identification Number (TIN). Form 10F, in this scenario, completes the missing details and ensures compliance with the DTAA rules.
So, this was all about Form 10F and when it is required by the NRIs. Moving further, let's know how NRIs can obtain a TRC.
Step-by-Step Guide to Obtain a Tax Residency Certificate for NRIs
NRIs who earn income in India need to provide a TRC from their resident country to claim the DTAA benefits. To obtain the certificate, they require the following information:
- Name of the taxpayer
- Status of assesse, i.e., individual, company, firm, etc.
- Permanent Account Number (PAN)
- Nationality (in case the taxpayer is an individual) or country of registration (in case of a business/ company)
- Tax Identification Number (TIN) of the Assessee
- Under section 90 (4) or section 90A (4), the period of residential status.
- Overseas address of the assessee.
Further, from country to country, the TRC format may differ. Hence, if the following information is not mentioned in the TRC issued by the foreign country, NRIs need to fill Form 10F and state these details in it.
Additionally, taxpayers before the end of the financial year can renew their TRCs to enjoy the DTAA benefits. It can be done by submitting the updated documents and fulfilling the renewal requirements stated by tax officials. However, this process is not quick, and from country to country, the process time can vary. Therefore, it is advisable to apply for the tax residency certificate before the end of the specific financial year.
From tax obligations to compliance, Savetaxs makes it simple.
Final Thoughts
Lastly, in today's globalized world, a tax residency certificate (TRC) has become a vital document for individuals and businesses. It helps them in smoothly conducting cross-border financial transactions and avoiding double taxation. So, whether you are a resident of India, earning income from overseas, or an NRI with an Indian income, TRC certifies that you did not pay taxes on the same income twice.
Further, being an NRI handling the Indian tax obligations can be difficult. Let Savetaxs assist you in this. Our financial experts ensure accurate filing of your returns, and while maximizing your refunds, help you claim the tax benefits under DTAA. Connect with us today and resolve your tax obligations without any issue.
Note: This guide is for information purposes only. The views expressed in this guide are personal and do not constitute the views of Savetaxs. Savetaxs or the author will not be responsible for any direct or indirect loss incurred by the reader for taking any decision based on the information or the contents. It is advisable to consult either a CA, CS, CPA or a professional tax expert from the Savetaxs team, as they are familiar with the current regulations and help you make accurate decisions and maintain accuracy throughout the whole process.

Mr Varun is a tax expert with over 13 years of experience in US taxation, accounting, bookkeeping, and payroll. Mr Gupta has not prepared and reviewed over 5000 individual and corporate tax returns for CPA firms and businesses.
- Section 9 Of The Income Tax Act
- Sections 90, 90A & 91 of the Income Tax Act for NRIs
- Section 89A - Tax Relief on Income from Foreign Retirement Funds
- NRI Selling Property in India
- Your Complete Guide on TCS on Foreign Remittance
- Form 27Q Simplified For NRIs- TDS Return on Payments
- Section 80C of Income Tax Act - 80C Deduction List
- Income Tax Form 13 For NRIs - Lower or Non Deduction
- Everything You Need to Know About Form 15CA and 15CB of Income Tax
- TDS on Sale of Property by NRIs in India
Want to read more? Explore Blogs
Frequently Asked Questions
No matter what your source of income is, we've got you covered. There’s a plan for everybody!
_1758631896.webp)





_1766561286.webp)






_1766644785.png)