The IT (Income Tax) department categrises taxpayers based on their source of income and several other factors to ensure easy compliance by everyone. Income tax returns (ITRs) are documents used by taxpayers to report their income, claim deductions, and declare their tax liability to the Income Tax Department of India. There are seven types of ITR forms in India. ITR-2 is one of these forms that can be filled by individuals and HUFs who are receiving income other than income from "profit or gains from business or professions". In this guide, we will understand the meaning of ITR 2, who can file Form ITR-2, the key changes that were added, and how to file Form ITR-2.
Key Takeaways
- ITR-2 is used by individuals and HUFs to file their ITR when they don't have any earnings from a business or a profession.
- You are required to declare your salary, property income, capital gains, and eligible deductions while filing ITR-2.
- ITR-2 is divided into several parts and income Schedules.
- The last date to file ITR for FY 2024-2025 (AY 2025-2026) is the 15th of September, 2025.
- Late filing may incur penalties and interest charges.
- A new schedule is added to compute income acquired from cryptocurrencies or other virtual digital assets (VDAs).
What is ITR-2?
Form ITR-2 is used by individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) to file their income tax returns when they don't have any earnings from a business or a profession. Generally, it is used by those individuals who are getting their income from sources like salary, pension, capital gains, or any other sources.
Who is Eligible to File Form ITR-2 for FY 2024-2025
If you don't know who can file ITR-2 for the FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-2026), then to clear your confusion, the ITR-2 form is for individuals, NRIs, and HUFs who are getting income from the following sources:
- Income from salary/pension
- Income from house property in India from one or more house properties
- Resident not ordinarily resident (RNOR) and non-residents.
- Capital gains, both short-term and long-term
- Agricultural income less than INR 5000
- Income from other sources, such as interest gains and lottery winnings, etc.
You can file ITR-2 even if your total income from these sources exceeds ₹50 lakhs, provided you do not have income from business or profession.
Who is Not Eligible to File the ITR-2 Form?
- If they are a director of a company in India.
- NRIs receiving income from either a business or a profession in India.
- If they trade in shares, F&O, or crypto as business income.
- They get income from a partnership firm or LLP.
If the NRI meets any of these conditions, they must use the ITR-3 form instead of the ITR-2 form.
What are the Key Changes Made in ITR-2 Form for AY 2025-2026?
The major changes made in the form ITR-2 for FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-2026) are listed below:
| Area of Change | Details |
|---|---|
| Capital Gains Split | Capital gains need to be split depending on the transfer date: before or after 23rd July 2024 |
| Assets and Liabilities | Only need to be reported if the total income exceeds Rs 1 crore (raised from the previous limit) |
| TDS Section Reporting | Taxpayers must mention TDS section codes in "details of TDS deducted" to ensure better accuracy, such as 195, 194I, etc. |
| Buyback Loss Reporting | From 1st October, 2024, capital losses on share buybacks are permitted if the related dividend income is also reported under "Income from Other Sources" |
| RNOR/Non-Resident | For an NRI, ITR-2 is the standard form unless income from a business/profession is involved. |
What is the Structure of ITR-2?
ITR-2 is divided into a few parts for an NRI, which are as follows:
General Information & Tax Filing Sections
- Declaration by the taxpayer
- Return Preparer Section: Information to be filed only if a tax return preparer has prepared the return
- Tax Payments: Details of payment of advance tax, self-assessment tax, and TDS
- Part A: It will include general information. In this, you need to disclose your residential status.
- Part B-TI/Part B-TTI: Computation of total income and tax liability on total income
Income Schedules
- Schedule S: Salary income details only if earned from India
- Schedule HP: Contains details of income from house property in India, like rent received
- Schedule CG: Calculation of income under capital gains from shares, property, or mutual funds in India
- Schedule OS: Income from NRO, dividends, or other income sources in India
- Schedule E I: Exempt income details like NRE interest (if applicable)
- Schedule PTI: Details of pass-through income from business trust or investment funds in India as per Section 115UA, Section 115UB
- Schedule VDA: Income from the sale of crypto or virtual digital assets in India
- Schedule S I: Statement of income, which is liable to special income tax rates, like LTCG/STCG
- Schedule 112A: Sale of a company's equity share or a unit of equity-oriented fund/business trust in which STT is paid
- Schedule 115A (1)(b)0iii) proviso: It is specifically for NRIs for the sale of equity shares of a company or a unit of equity-oriented fund/ business trust, where STT is paid
Get trusted guidance for NRI tax filing, planning, and cross-border strategies with ease.
Foreign Income / Assets & DTAA
- Schedule FA: Declaration of foreign assets and income from any other source outside India
- Schedule TR: Details of taxes paid outside India, required to claim DTAA relief
- Schedule FSI: Statement of income accrued or received outside India (if taxable in India under RNOR/DTAA)
Losses & Set-Off
- Schedule CYLA: Income statement after set off current year's losses
- Section BFLA: Income statement of set off of unabsorbed loss brought forward from previous years
- Schedule CFL: Statement of losses to be carried forward to future years
Deductions
- Schedule VIA: Deductions from total income under Chapter VI-A, such as 80C, 80D
- Schedule 80G: Donation statements entitled for deduction u/s 80G
- Schedule 80GG A: Statement of donation for scientific research or rural development
- Schedule 80GGC: Statement of contribution made to political parties
- Schedule 80DD: Deduction details in respect of maintenance, including medical treatment of a person who is dependent due to disability
Special Tax Computations
- Schedule AMT: Calculation for those subject to the alternative minimum tax payable under Section 115JC
- Schedule AMTC: Computation of tax credit under Section 115JD
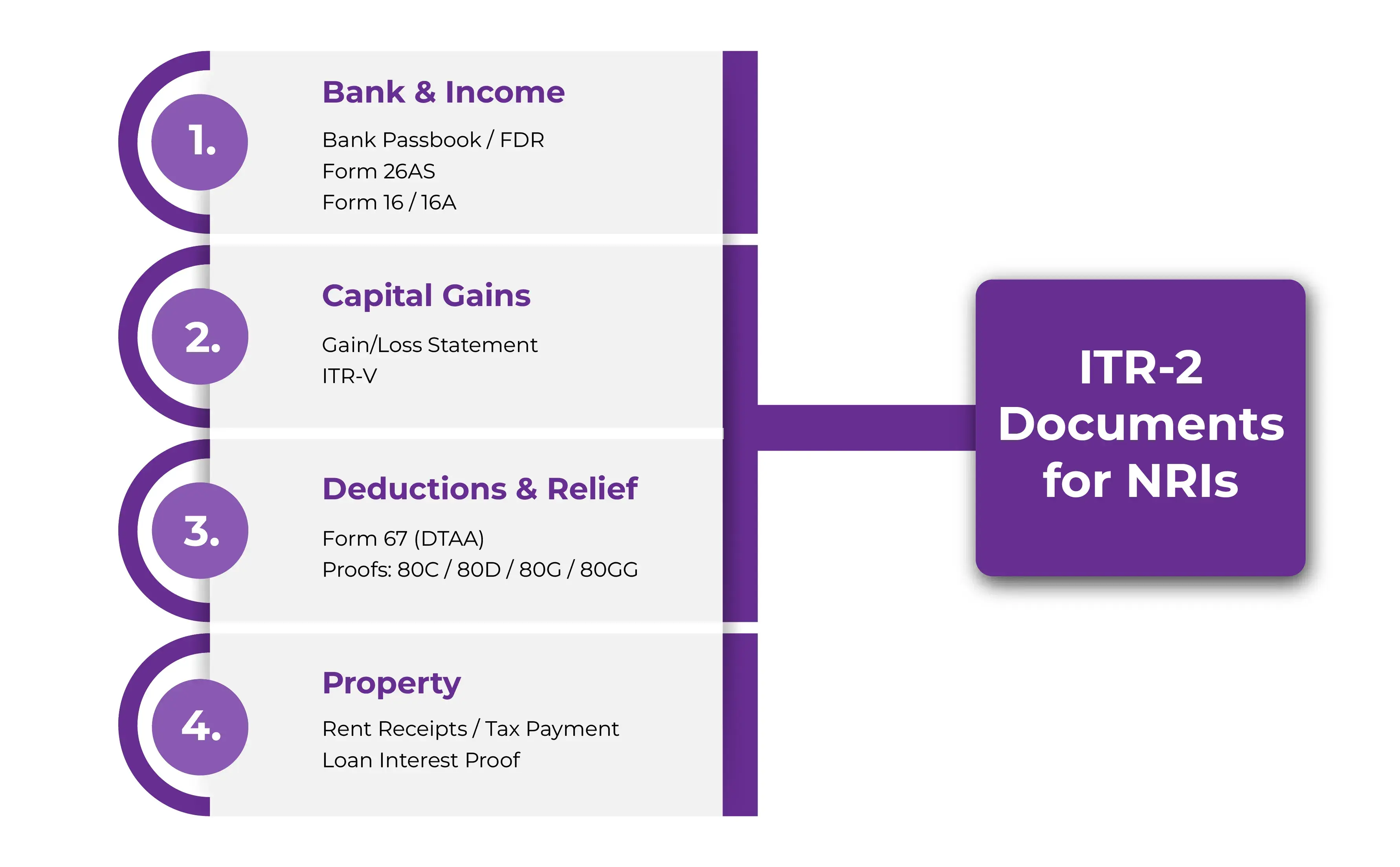
What Documents Are Required to File ITR-2 for NRIs?
- Bank Passbook/ FDR receipts: To calculate the amount of interest income from a savings account or an NRO Account
- Foreign Tax Credit (Form 67): Essential for NRIs, if claiming relief under the DTAA Act
- TDS Certificate (Form 16A): If you have earned interest on NRO fixed deposits, savings, etc., and TDS has been deducted on the same, get Form 16A issued by the deductor
- ITR-V: You will require a copy of ITR-V, with reference to the previous year, mentioning the said loss. If you want to carry forward the previous year's losses
- Rent Receipt/Local Tax Payment: If you are earning rent from an Indian house property, then you will require your tenant/local tax payment/ interest on borrowed capital details (if any) to calculate income and deductions from house property
- Document to Claim Losses: If claiming losses from capital gains, house property, or other sources in India during the current year, you will require the relevant document stating the loss
- Form 26AS: To determine TDS on your Indian income, like salary, rent, interest, etc, you will require Form 26AS. This form can be downloaded from the e-filing portal.
- Proof of Deductions Under 80C/80D/80G/80GG: You will also require documents or proofs for claiming tax savings deductions under section 80C, 80D, 80G, and 80GG, like life and health insurance receipts, donation receipts, rent receipts, tuition fees receipts, etc. if not claimed via employer or were not mentioned in your Form 16
- Form 16: If you have a salary income, you will need Form 16 issued by the employer.
- Capital Gain Statements: If you have any capital gains transactions in shares, then you will require a summary or profit/ loss statement of capital gain transactions of shares or securities during a year, if any, for the calculation of capital gains.
Key Changes Made in ITR-2 for NRIs in AY 2023-2024 and AY 2024-2025
The following changes are added in the ITR-2 form for the FY 2022-2023, and also applicable for FY 2023-2023:
- Schedule 80G Clauses D-ARN required: Additional details are required in Schedule 80G Clause D for ARN (Acknowledgement Reference Number) if claimed donations.
- Relief u/s 89A: A clause has been added related to relief to NRIs with a foreign retirement benefits account, like 401(k), IRA, or superannuation. Applicable if tax is delayed in the foreign country.
- Point No.1(e)4: Income subject to taxes during the previous year on which relief was claimed u/s 89A in any earlier year
- Schedule VDA: NRIs receiving income from the sale of virtual digital assets, a new schedule is added to calculate income from cryptocurrencies or other virtual digital assets (VDAs)
- Schedule SI (Section 115BBH): A new point added 115BBH, in which Income from Virtual Digital assets is taxed at 30% without deductions.
Common Errors to Prevent
Carefully considering accuracy and completeness while filing the ITR-2 form is vital to claim the benefits. Here are some of the common mistakes to avoid while filing the ITR-2, along with the impact the mistake could make and ways to prevent them:
Failing to Disclose Foreign Assets
- Mistake: An NRI who has become a resident again, forgetting to declare foreign assets or foreign-sourced income (if any)
- Impact: Will be considered a violation of the tax laws and may attract heavy penalties under the Black Money Act
- Prevent: Make sure to disclose foreign-sourced income and any income earned from foreign assets as per the rules of the Black Money Act or any other laws as applicable.
Not Reporting All Sources of Income
- Mistake: Not disclosing other Indian income sources, such as rental income, bank interest, capital gains, or agricultural income (if applicable)
- Impact: Not reporting or underreporting may attract penalties
- Prevent: While filing the tax returns, ensure to declare all Indian-sourced income, even if it seems a small amount, or even if income earned abroad is exempt
Errors in Personal Information
- Mistake: Mentioning old or wrong personal details, like address, bank account number, contact number, or mispelling your name.
- Impact: Refunds might get delayed, and problems may arise during ITR processing
- Prevent: Ensure to cross-verify all information before submitting the form.
Delay in Filing
- Mistake: Filing a return after the due date
- Impact: Filing late may attract penalties as well as interest on due taxes
- Prevent: An NRI must stay well-prepared to file the Income Tax Return (ITR) before the deadline to avoid any issues at the last moment.
Missing Calculation of Capital Gains
- Mistake: Wrong or missing calculation of capital gains from the transfer of property, shares, or mutual funds in India
- Impact: May attract penalties and might result in overpayment or underpayment with financial differences
- Prevent: Calculate gains using actual data related to purchase and sale prices. Also, use accurate rates against short-term and long-term capital gains.
Incorrect Deductions
- Mistake: Claiming deductions that are not available to NRIs, such as 80DD, 80DDB, 80U, or missing valid deductions, like 80C, 80, 80E
- Impact: Higher tax liability or loss of benefit to save on taxes
- Prevent: Check all the eligible deductions and sections available for an NRI and apply them accordingly. Also, ensure to provide supporting documents to support your claim.
How to File ITR-2 Online as an NRI?
Filing an ITR-2 online has a well-structured process. With a little systematic approach, the process can be managed easily. Follow the steps mentioned below for filing ITR-2:
Step 1: Gather and Prepare all the Required Documents
Gather Form 26AS, bank statement, capital gains details, foreign income details, information about loans/investments, proof of deductions, and Form 16 (if worked in India). NRIs must mainly focus on Indian bank accounts and property, and must determine which deductions an NRI is eligible to apply for.
Step 2: Register or Log in to the e-Filing Portal
Visit the Income Tax e-filing portal. In case you are a new user, log in by entering your PAN number, using it as your User ID. If you have already registered, enter your user ID, password, and the captcha code to log in.
Step 3: Download ITR Utility/Prepare Online
Opt for the online method to experience an easy process, or you can download the utility. If you want to file the ITR-2 form online, click on "Downloads" to use the utility provided by the Income Tax Department. However, if you are an NRI staying abroad, file it online directly through the portal. Click on "e-file" and then ITR, after that click on "file income tax returns".
Step 4: Choose the Assessment Year
Always check the relevant year to avoid any mismatch later. For the financial year 2024-2025, choose assessment year 2025-2026.
Step 5: Mode of Filing
Select the mode using which you would like to file your return. Choose the "online filing" option through the portal and ensure good internet connectivity, and try to avoid filing offline to experience an easy process.
Step 6: Fill ITR-2 Form
Fill out your personal and income details in the form accurately, including Indian assets, tax paid, TDS, Capital Gains, and eligible deductions. Also, ensure to mention your NRI status correctly and any foreign income that is taxable in India.
Step 7: Pay Taxes (if payable)
It is often required if the NRI sells a property or receives rental income. If the tax is payable after determining TDS and advance tax, then use the challan link and enter the challan details in the tax return.
Step 8: Preview and Submit your ITR
Cross-verify all the entered information and ensure they are accurate, especially your residential status and summary of Indian income. Once ensured that everything is correct, submit your ITR. You will be redirected to verify your return page upon submitting your ITR.
Step 9: Verify the Returns
Your ITR will not be considered complete until you do the verification. You can complete the verification through a variety of options, such as receiving an OTP via Aadhaar number, sending a signed physical copy of ITR-V to CPC, Bengaluru, and using your bank account. Usually, NRIs either choose to file their ITR through net banking or by courier.
Step 10: Download Acknowledgement
Download the acknowledgment after verification, which was earlier called ITR-V. Keep a copy of the filed ITR and the acknowledgement for future reference.
Step 11: Track Processing
You can log in to the e-filing portal and track the status of your ITR. Verify the processing of your ITR to ensure that it has been accepted and processed without any issues. This is to ensure you are aware of any steps that need to be taken from your side.
To Conclude
As an NRI, you need to choose the correct ITR form based on your income source, capital gains, and financial holdings in India to avoid any issues. Choosing the right form will ensure that you experience faster processing, right tax compliance, and can also avoid any issues or notices.
Do you find the Income Tax for NRIs filing complex, and are you unsure of which ITR form needs to be filed? Don't worry, Savetaxs experts can help you file your ITR with the correct Form. Our team of professionals with more than a decade of experience can help you avoid paying penalties and getting a tax notice by assisting you with every tax complexity. Claim what is legally yours with the help of Savetaxs.
Speak to our experts and get personalized solutions for your NRI tax needs
View Plan- What is ITR 3 and How Can an NRI File It Online?
- Penalty for Late Filing of Income Tax Return for NRIs
- Income Tax Notice: Check and Authenticate Online
- What is ITR-U (Updated Income Tax Return) for NRIs?
- Common ITR Filing Mistakes NRIs and Indian Residents Make
- Form ITR-V: How to Download Your ITR-V from the Income Tax Portal?
- Old vs New Tax Regime: Which is Better for NRIs
- PAN Card for NRIs - Comprehensive Guide
- NRI Income Tax in India (2025): Rules, Slabs, Capital Gains & ITR Forms
- What Is Form 16: A Comprehensive Guide
- What is the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Singapore?
- Everything You Need to Know About Form 15CA and 15CB of Income Tax
- TDS on Sale of Property by NRIs in India
- NRE & NRO Accounts - Meaning, Comparison, Benefits, Taxation
- TDS Certificate Form 16A For NRIs: TDS on Indian Income
- Section 54F of Income Tax Act - Exemption on Purchase of Residential Property
- Form 61A Income Tax: Applicability, Due Date & How to File SFT Online

Mr Varun is a tax expert with over 13 years of experience in US taxation, accounting, bookkeeping, and payroll. Mr Gupta has not prepared and reviewed over 5000 individual and corporate tax returns for CPA firms and businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are you not sure if ITR-2 applies to you? Our FAQs explain it in detail for NRIs.
No, a balance sheet is not compulsory for a salaried individual who is filing their income tax return using the ITR-2 form.
The deadline for filing ITR 2 returns is 15th of September 2025 for the financial year 2024-2025 (Assessment year 2025-2026).
Yes, an NRI has to use ITR-2 to report their Indian assets and liabilities.
The processing time for ITR-2 is nearly 9 months from the end of the financial year in which the individual has furnished the return. However, in many cases, ITR is processed within 7-30 days after e-verification.
There are two parts in the ITR-2 form. Part A includes the basic information, while Part B includes the calculation of the total income and tax due on the complete earnings of the individual.