The DTAA (Double Tax Avoidance Agreement) between India and the UK is an initiative made by the Indian government to prevent residents of both nations from being taxed twice on the same income. The Indian Government has signed DTAAs with almost 100 countries worldwide.
It allows different types of tax relief and deductions. Also, the taxes paid in one country can be claimed as a credit in another country under this tax treaty. An NRI or a business operating in both nations must understand this agreement to reduce their tax liability and ensure compliance.
In this blog, we will learn about the DTAA between India and the UK and understand the details for avoiding double taxation.
- The DTAA between India and the UK was signed on 26th October, 1993, to prevent double taxation on the same income earned in either country.
- The agreement offers several benefits, including a boost to global trade, tax reliefs and exemptions, capital gains relief, etc.
- The TRC (Tax Residency Certificate) and Form 10F are two essential documents required to avail the benefits of DTAA. These form the core of TRC and Form 10F for NRIs, especially for those dealing with UK NRI tax on Indian income.
- TRC is a certificate issued by the tax authorities of the NRI's country of residence to prove they are a tax resident of that country.
What is the DTAA Between India and the UK?
On 26 October 1993, India and the UK agreed to abide by the articles included in the DTAA and signed the agreement. With this agreement, both India and the UK can avoid paying taxes twice on the income earned in either country. An individual, a company, or an entity operating across India and the UK qualifies for the DTAA.
Anyone who resides in the UK for at least 182 days in a financial year can claim tax exemptions under the UK-India DTAA. This agreement consists of 31 articles and a few sub-sections that elaborate on the rules for claiming tax benefits by a tax resident of either nation.
What are the Benefits of the India-UK DTAA?
The India-UK DTAA offers several benefits to an NRI, which help them reduce their tax burdens, including:
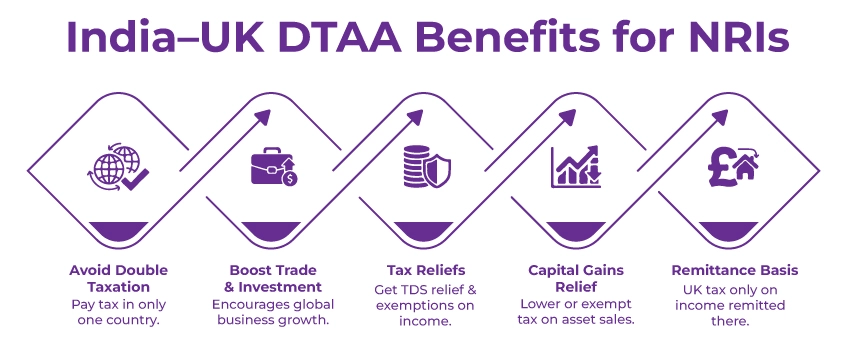
- Avoid Double Taxation: Taxpayers are responsible for paying taxes in only one country, per the treaty's provision. It means they can avoid being taxed twice on the same income in two different nations.
- Boost to Global Trade: This treaty improves opportunities for employment and investments, allowing businesses to expand worldwide without the risk of facing excessive tax burdens.
- Tax Reliefs: It provides tax relief on TDS, tax credits, and exemptions for specific income categories. It can include dividends, royalties, and interests.
- Capital Gains Relief: Gains from the sale of an asset may be eligible for lower tax rates or exemptions under specific treaty provisions, helping avoid excess taxation.
- Remittance-Based Taxation: The residents of the UK are liable to pay tax only on income actually brought into or remitted to the UK.
What are the Types of Taxes Covered Under the India-UK DTAA?
The DTAA applies to two categories—United Kingdom Tax and Indian Tax.
Under DTAA, taxes that fall under the 'United Kingdom Tax' are:
- Income Tax
- Corporate Taxes
- Taxes on Capital Gains
- Taxes on Petroleum Revenue
Taxes in the 'indian Tax' category are:
- Income tax (including all applicable surcharges)
- Taxes with a similar nature that were introduced later
Key TDS Rates Under the India-UK DTAA
These are some of the India-UK DTAA TDS rates:
Dividends (Article 11):
- Tax on dividend income received from an immovable property: 15%
- For other dividends: 10%
- Taxpayers may claim a 15% tax credit for the dividends received.
Interest (Article 12):
- General interest income: 15%
- Interest paid to a banking institution: 10%
- Government and central bank-related interest payment: Tax-exempt.
Royalties and Technical Services (Article 13):
- Royalties and technical services are taxed at 15%
- Specific technical services during the initial treaty years may be charged at 20%, with a cap of 15% later.
Taxation of Capital Gains Under DTAA
Generally, capital gains are taxed under the domestic laws of India and the UK. It applies until they are specifically exempted under the treaty. Additionally, gains from air transportation and shipping contracts often qualify for the relief (Articles 8 and 9).
How NRIs Can Claim DTAA Benefits?
An NRI must follow the steps below to claim the benefits of the DTAA tax treaty:
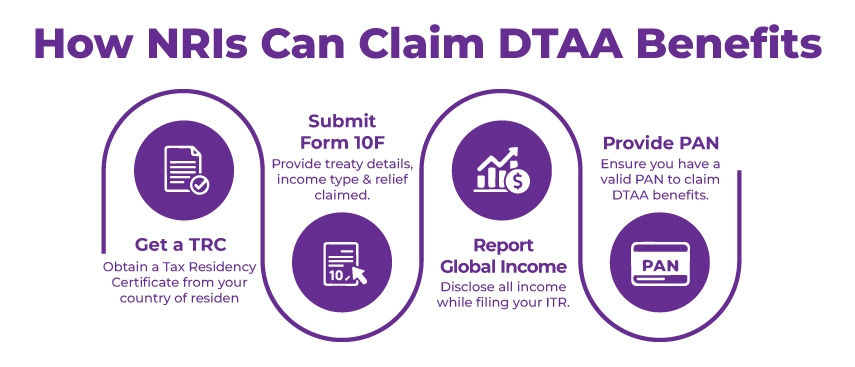
Step 1: Obtain a TRC
Firstly, an NRI must get a TRC (Tax Residency Certificate) as it is an essential document required to avail the DTAA benefits. The TRC will be issued by the tax authorities of the NRI's country of residence. It will prove that the NRI is a tax resident of the country.
Step 2: Submit Form 10F
NRIs must fill Form 10F with the treaty's name, the income type, and the tax relief claimed. You must submit this form along with the TRC.
Step 3: Report Global Income in the ITR
Now, you must pay your taxes abroad and report your global income when filing your returns. You must report the accurate income to ensure compliance and avoid hefty penalties.
Step 4: Submit a Valid PAN
To claim the benefits under the DTAA, a PAN must be submitted. An NRI may face difficulties in claiming the relief if there is no PAN (Permanent Account Number).
What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing DTAA?
Filing a DTAA comes with several benefits, but furnishing an improper application may attract problems. The following are some of the common mistakes that an NRI must avoid:
- Not Providing Proper Documents: Completing the paperwork accurately is essential for a smooth process. Missing any vital documents, such as a TRC or Form 10F, can result in benefits being denied.
- Overlooking Residency Status: Your tax liability is determined in large part by your residency status. You need to stay aware of your residency status in both nations.
- Failing to Report Income Accurately: Even if your income is exempt under DTAA, you must report it in both countries. You may attract a hefty penalty if you misreport your income.
- Ignoring TDS Rates: You need to determine the specific tax rates under the treaty to avoid excess TDS on Indian income.
To Conclude
Understanding the DTAA between India and the UK is very important. It not only avoids double taxation but also provides significant tax benefits to the taxpayer. Proper documentation, such as a valid TRC, Form 10F, is vital to claim these benefits. However, one must understand its provisions to maximize the benefits, which may seem complex to some.
Given its complexity, seeking help from the experts at Savetaxs can be a wise decision. We have an entire team of experts who can help you understand and claim the DTAA to maximize your benefits. Our team can help you enjoy the process with utmost convenience, accuracy, and peace of mind. Contact us anytime, as we are working around the clock globally to help you resolve all your tax queries.
**Note: This guide is for informational purposes only. The views expressed in this guide are personal and do not constitute the views of Savetaxs. Savetaxs or the author will not be responsible for any direct or indirect loss incurred by the reader for taking any decision based on the information or the contents. It is advisable to consult either a CA, CS, CPA, or a professional tax expert from the Savetaxs team, as they are familiar with current regulations and can help you make accurate decisions and maintain accuracy throughout the process.

Mr Manish is a financial professional with over 10 years of experience in strategic financial planning, performance analysis, and compliance across different sectors, including Agriculture, Pharma, Manufacturing, & Oil and Gas. Mr Prajapati has a knack for managing financial accounts, driving business growth by optimizing cost efficiency and regulatory compliance. Additionally, he has expertise in developing financial models, preparing detailed cash flow statements, and closing the balance sheets.
- Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Australia
- A Comprehensive Guide on the DTAA between India and the USA?
- Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Oman
- What is the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Singapore?
- Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Hong Kong
- Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Mauritius
- Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Canada
- Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and China
- Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Japan
- What is Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)? How NRIs can Claim Benefits Under DTAA
Want to read more? Explore Blogs
Frequently Asked Questions
No matter what your source of income is, we've got you covered. There’s a plan for everybody!
Ans: DTAA covers various types of income, such as:
- Capital gains
- Pensions and annuities
- Royalties and technical services fees
- Interest and dividends
- Salary or employment income
- Business or professional income
Ans: The DTAA can be classified depending on the number of countries involved:
- Bilateral DTAA: It is the common form of DTAA, signed between two countries like India-UK or India-USA.
- Multilateral DTAA: It is signed between multiple countries and is less common.















_1766559165.png)