US taxpayers use IRS Form 1040 to file their individual tax return. Depending on the taxpayer's income source and deductions, they may also need to file other types of Form 1040, such as Schedule A or Schedule C. This form allows US taxpayers to report their annual income, claim tax credits, and calculate their tax refund or liability.
In this guide, we will cover everything you need to know about Form 1040, including how to file it, so you're prepared for the next tax filing season.
Key Takeaways
- US taxpayers use Form 1040 to report their annual income and claim eligible tax adjustments known as above-the-line deductions. The computation in question yields the adjusted gross income (AGI) of the taxpayer.
- If the taxpayer is 65 or older, they might want to use Form 1040-SR. This version of Form 1040 is printed with larger fonts, making it easy for senior citizens to read, and it also has a chart to specify the standard deduction.
- If the taxpayer is a non-resident alien, then they must file Form 1040-NR.
- If the taxpayer wishes to amend a previously filed Form 1040, they must use Form 1040-X.
What is Form 1040
The IRS Form 1040 is an official document that U.S. taxpayers use to file their annual income tax returns. This form is divided into sections where the taxpayer must report their deductions and income to compute the taxes they owe or the refund they expect to receive.
Depending on the source of your income, you report the requested information; however, in some instances, the taxpayer might need to attach a few additional forms known as schedules. However, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) updates the form annually to reflect changes in tax laws, inflation, and other applicable updates.
What are the Different Versions of the 1040 Form?
As Forms 1040A and 1040EZ are no longer available, there are now four variations of Form 1040. Which are as follows
Form 1040: This is the standard form used by most taxpayers to report their annual income, refunds, or additional tax owed.
Form 1040-SR: This version of Form 1040 is for senior taxpayers who are 65 or above. Form 1040-SR is generally identical to the standard Form 1040, but it is printed in a larger font and includes a chart to help determine the standard deduction.
Form 1040-NR: This form is used by non-resident aliens, and as compared to the other version of the 1040 form, it is several pages longer.
Form 1040-X: This version is used by individuals who wish to amend their tax return.
Why are the Short-Form Versions, 1040A and 1040EZ, No Longer Available?
The 1040A and 1040EZ versions were removed from the tax reform. The IRS then consolidated both forms into one, allowing taxpayers to use schedules instead.
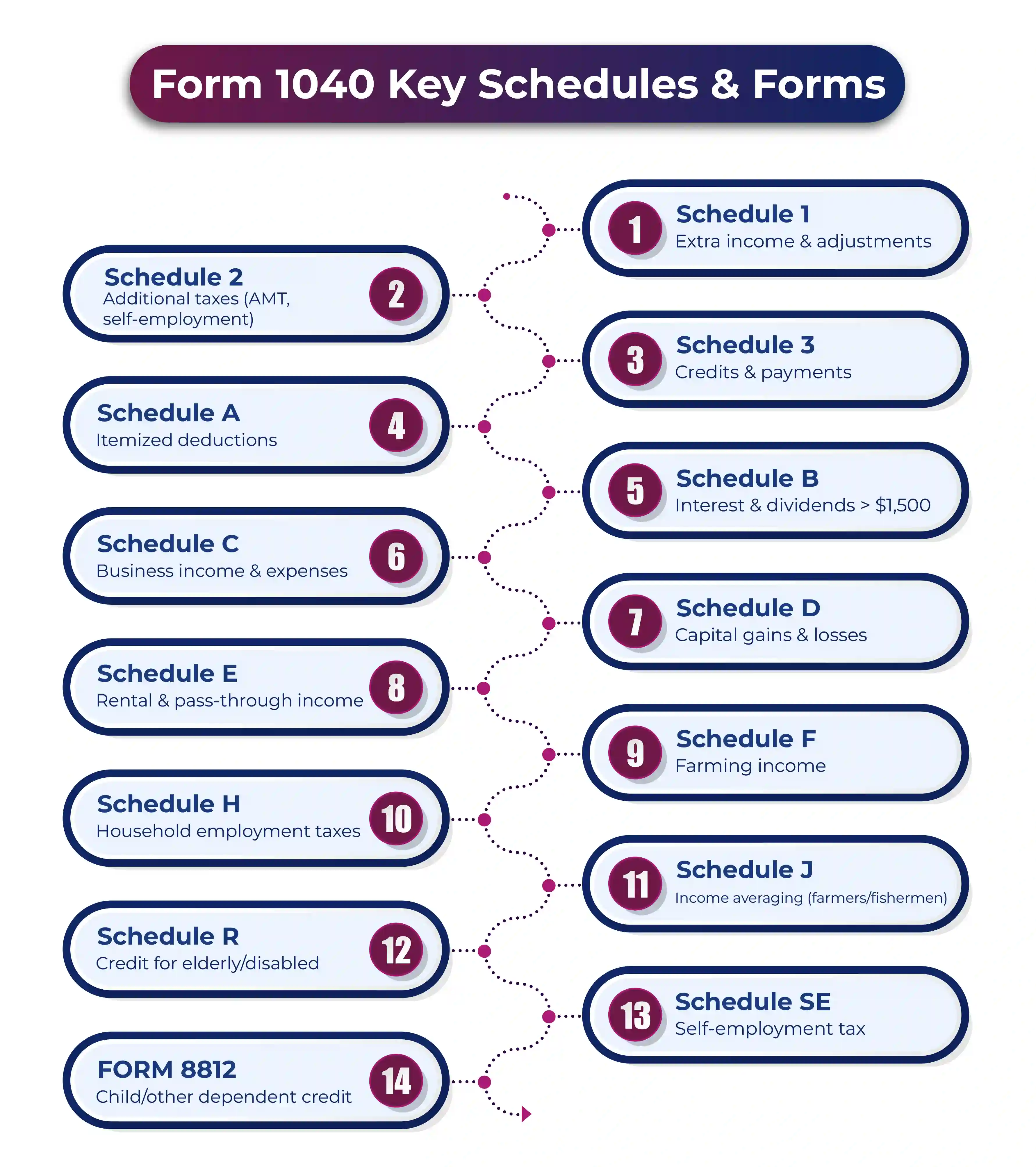
What are the Schedules Used in Form 1040?
There are various schedules and additional forms that support the Form 1040, helping US taxpayers calculate certain items applicable to Form 1040.
- Schedule 1: This schedule or form is used for reporting different common income sources or adjustments made to one's income.
For example, Schedule 1 includes gains or losses from the sale of a commercial/business property, alimony, compensation received from unemployment, business income, expenses of an educator, student loan interest deduction, and contributions made towards a health savings account. - Schedule 2: This schedule or form is used by US taxpayers to report any additional attachments and Schedule 2 forms of the reports. The first part is used for the alternative minimum tax and the repayment of previously claimed tax credits for health insurance purchased through the insurance marketplace.
The second part of the form is used for reporting self-employment taxes, Medicare tax, and other additional taxes, including those on IRAs, household employment taxes, repayment of the first-time home buyer credit, net investment income tax, and more. - Schedule 3: This form or the schedule is used for reporting additional payments or credits. Schedule 3 is divided into two parts: refundable credits and non-refundable credits.
The credits reported under these segments include credits for expenses associated with child and dependent care, credits for residential energy, excess tax payments made in previous years, overpaid social security taxes made in previous years, and more. - Schedule A: This is a common form used by U.S. taxpayers to enter all itemized deductions.
This includes dental or medical expenses, mortgage interest, local and state taxes, theft or casualty losses, charitable donations, and other similar costs. - Schedule B: This schedule form is used for reporting dividends and interest income that are above the threshold of $1,500. For taxpayers with income from interest or dividends exceeding the threshold, they can enter it directly on Form 1040, Lines 2 and 3.
- Schedule C: This form is used by taxpayers to report the profits or losses of their business. Contractors working independently, freelancers, sole proprietors, and sole members of LLCs use this form to report their earnings and losses.
- Schedule D: This form is used by US taxpayers to report their capital gains or losses made from investments.
- Schedule E: Individuals with profits or losses from rental real estate, partnerships, royalties, estates, trusts, S corporations, REMICs, or other pass-through entities will use Schedule E to report their details.
- Schedule F: Farmers use this form to report their income as well as the expenses related to farming.
- Schedule H: Individuals who are nannies or caretakers use this form. Because in such a case, the taxpayer is obligated to withhold income for Social Security and Medicare taxes. Such taxes are reported under Schedule H.
- Schedule J: This schedule form is used for reporting income averaging from fishermen and farmers. Averaging the previous three years of taxes to have a more distributed tax liability.
- Schedule R: This form is used by individuals who want to claim the diversity tax credit.
- Schedule SE: This schedule form is used by independent contractors or business owners to calculate the self-employment tax when they have made at least $400 in profits.
- 8812: For claiming credit for other dependents or the child tax credit, use this form.
How to Fill Out Form 1040?
Below is an outlined process stating how one should fill out their Form 1040
Step 1: Begin by entering all your personal information. The top part of the form provides a space for the taxpayer to enter their personal information, including their social security number, name, address, and filing status. In a case where the taxpayer is filing a joint return, they must not use their spouse's Social Security number either.
Step 2: After filing your personal information, the next step is to gather your W-2 forms from your employer(s) or any 1099 forms for reporting income from additional sources, such as freelance work or investments. Ensure that you do not miss any form, and please double-check every report for accuracy.
Step 3: This is where you will claim the tax deductions. You must explore the various deductions available to you and the qualifications for each one. Such tax deductions help taxpayers reduce their taxable income.
Some common deductions include educator expenses, student loan interest, and contributions made to retirement accounts. Be sure to have the appropriate documents handy for precise income reporting.
Step 4: Now, either take the itemized deduction or the standard deduction. This is where the taxpayer decides which deduction they will choose.
The IRS has set the standard deduction amount, whereas itemizing deductions allows taxpayers to list the specific expenses. Then, you can evaluate which opinion is more beneficial for you.
Step 5: Another good way to lower tax liability is by claiming tax credits. The taxpayer can explore tax credits, such as the Child Tax Credit, the Earned Income Credit, or the Educational Credits.
However, you must ensure that the set eligibility criteria are met and you have all the needed information to claim these credits accurately.
Step 6: If the taxpayer has self-employment income, they must calculate the self-employment tax. Likewise, if the tapyer has a househelp or the caretaker, then they must owe the household employment tax.
Hence, one must ensure that they report all such taxes and income accurately on their Form 1040, using the correct schedule and form to determine if taxes are owed.
Step 7: Lastly, include all payments made throughout the year. And also specify how you wish to receive the tax refund, if any, either through direct deposit or by check.
Avoid penalties and stay stress-free with expert IRS tax compliance services. Our team ensures every return is prepared correctly and submitted before deadlines.
Start Filing TodayWhere to File your Income Tax Form 1040
The way you are filing the form will depend on where you must file Form 1040.
For Paper Filers: In cases where the taxpayer is filing a paper return, they must mail the return to the designated address. The address of the mail will depend on where you have filed the return.
The IRS has listed all the appropriate mailing addresses, state by state, on its official website. However, please note that the paper return process can take several weeks to complete due to certain factors, such as staffing shortages.
For the fast processing of your return, the IRS encourages you to file electronically.
For electronic return filers: The taxpayer who is filing the return online can use the IRS do-it-yourself tax software. To process your return more quickly, connect with Savetaxs.
Expert Help in Filing Form 1040
Filing your tax returns in the US accurately and ensuring that you use the correct forms or schedules is crucial. However, with Savetaxs, we help ensure you get the best tax refunds possible while ensuring your tax returns are accurately filed by the deadline.
We have been helping U.S. residents and NRI individuals in India file their taxes for over a decade now. With an expert team of chartered accountants and tax experts who have a knack for Indian and foreign taxation, we assure you that your taxes are handled with utmost precision.
We are available 24/7 across all time zones, so connect with us to make your financial stress a thing of the past.
Speak to our experts and get personalized solutions for your NRI tax needs
View Plan- What is the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) Between India and Singapore?
- Everything You Need to Know About Form 15CA and 15CB of Income Tax
- TDS on Sale of Property by NRIs in India
- NRE & NRO Accounts - Meaning, Comparison, Benefits, Taxation
- TDS Certificate Form 16A For NRIs: TDS on Indian Income
- Section 54F of Income Tax Act - Exemption on Purchase of Residential Property
- Form 61A Income Tax: Applicability, Due Date & How to File SFT Online

Mr Varun is a tax expert with over 13 years of experience in US taxation, accounting, bookkeeping, and payroll. Mr Gupta has not prepared and reviewed over 5000 individual and corporate tax returns for CPA firms and businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
Clear and Concise Answers to the Most Frequently Asked Questions for Better Understanding and Guidance
The 1040 tax form is known as the U.S. individual income tax return form and is used by U.S. taxpayers, both residents and citizens, to report their annual income, claim eligible tax deductions, and calculate their tax liability and tax refund. The form must be filed with the IRS by every financial user.
Every US individual must file Form 1040 if their income exceeds the IRS threshold. This includes wages, salary, capital gains, interest, self-employment income, or, if you have specific income, obligations like health account contributions, self-employment tax, and more.
Information included in Form 1040 includes personal information, such as name, SSN, filing status of the taxpayer, and the dependents. The type of income sources being reported, including eligible deductions, tax credits, and more.
The variants of Form 1040 are Form 1040-SR, Form 1040-NR, and Form 1040-X.
- Form 1040-SR is for taxpayers aged 65 and above, as it features a simple layout and larger fonts.
- Form 1040-NR: This form is used by nonresident aliens who are earning in the United States.
- Form 1040-X: This form is filed to amend previously submitted 1040s.
The supporting schedules are Schedules 1, 2, and 3.
The Difference Between Form 1040 and Form 1040-NR is :-
- Form 1040 is for U.S. residents and resident aliens.
- Form 1040-NR is for non-resident aliens, e.g., NRIs with US investment or rental income from the United States.
Yes, you can file Form 1040 online.
NRIs only file Form 1040-NR if they earn any income from the US, such as rental income, dividends, capital gains from the US assets, and more.
Yes, you can amend it by filing Form 1040-X to correct the mistakes or update information.
Not really, NRI can claim tax relief under the DTAA between India and the US, using Form 1116 (FTC), at the time of filing Indian taxes.