- What is Section 54F of the Income Tax Act?
- Net Sale Consideration
- Eligibility Criteria to Claim Exemption Under Section 54F
- How to Calculate Tax Exemption Under Section 54F?
- What is the Difference Between Section 54 and 54F?
- What is the Capital Gains Account Scheme (CGAS)?
- Benefits of Section 54F of the Income Tax Act?
- How Can Savetaxs Help with Section 54F?
Whether an Indian Resident or an NRI, an increase in overall income has made tax planning an essential part of financial planning. Taxpayers are now seeking potential investment schemes to save on taxes. The Income Tax Act of India has various provisions that permit a taxpayer to claim an exemption, and one such provision is Section 54F.
This section of the Income Tax Act allows the taxpayer to claim a tax exemption on the sale proceeds of any capital asset, except for the residential property, by reinvesting the capital gain in the purchase or construction of a house property.
In this blog, we will explore Section 54F of Income Tax Act, covering who can claim, the amount of exemption available, and more.
- Under section 54F, NRIs can claim tax exemption on the sale of any capital asset other than residential property. This tax exemption is available on long-term capital gains.
- To claim tax exemption under section 54F, using the sale proceeds, you need to buy a new house.
- The new residential property should be purchased either 1 year before or 2 years after the sale. Additionally, the new property should be constructed within three years of the sale of the old property.
- You can claim up to INR 10 crore under section 54F of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
What is Section 54F of the Income Tax Act?
Section 54F of Income Tax Act states that individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) can avail a tax exemption on capital gains income made by selling an asset, including land, gold shares, or anything other than a residential house, and then reinvesting the sale proceeds in a new residential property within a given time frame.
Here is how Section 54F of the Income Tax Act works for capital gains exemption:
- The taxpayer is liable to invest the entire sale amount, not just the profit on a residential property.
- The taxpayer is permitted to buy a new residential house either one year before or two years after selling the old asset. Or the taxpayer has a timeframe of constructing a residential house within three years of the sale.
- The concerned taxpayer must not hold more than one house at the time they are selling the asset.
- Lastly, the taxpayer is not permitted to build or buy another house within the next few years, which is two years to purchase and three years to build a residential home.
Ensure that if any of the rules mentioned above to claim tax exemption under Section 54F are not met, the tax exemption is cancelled, and the entire capital gain will be taxable for the respective financial years.
Net Sale Consideration
For a taxpayer to qualify for the tax exemption on long-term capital gains, they must reinvest the net consideration sale proceeds from selling a non-residential asset in India into a new residential property.
Here is what net consideration means:
The total amount the taxpayer received by selling the assets is the full value of the consideration.
Now the seller must subtract any expenses that they have incurred specifically for the sale of the property, like the legal charges or the broker fees. Upon subtracting such charges, the amount left is the "net consideration" amount, which needs to be reinvested within the specified time frame.
Eligibility Criteria to Claim Exemption Under Section 54F
As mentioned above, to claim tax exemption under Section 54F of the Income Tax Act, the taxpayer must be:
- An individual, be it an Indian resident or an NRI, and a Hindu family (HUF) can claim tax exemption under Section 54F.
- To qualify for the tax exemptions, the concerned taxpayer must buy or construct a residential house in India either one year before or three years after the asset has been sold.
- The cost of the new residential house must either be equal to or more than the net consideration received from the sale of the original asset to be eligible for claiming a tax exemption.
- The tax exemption under Section 54F is not allowed if the taxpayer holds more than one house apart from the new one on the date of transfer.
How to Calculate Tax Exemption Under Section 54F?
Calculating a tax exemption under Section 54F is no rocket science; in fact, it is based on a simple formula. Here is how you can calculate the Section 54F exemption.
Let us understand it with an example:
Mr Khemraj sold a land to Mr. Raj on 10th July 2024 for Rs 5 Crore, which Mr Khemraj originally bought for 50 lakhs in May 2020.
In August 2025, he purchased a residential house for three crore.
So can Mr Khemraj avail an exemption under Section 54F? Let us see:
- He has held a property for more than two years, which will be classified as a long-term property, and the long-term capital gains rules will apply.
- He sold the non-residential assets and then again re-invested the sale proceeds in a residential house.
- He was not the owner of any other house at the time of sale.
- He bought a new residential house within two years of the date of sale of the original assets.
Yes, he is eligible for the tax exemption. So, here is the capital gains calculation:
| Particulars | Amount |
|---|---|
| Sale Price | 5,00,00,000 |
| Indexed Cost of Purchase (5,00,00,000 * 365 / 301) | 60,20,900 |
| Long-Term Capital Gain | 4,39,79,100 |
Now, let us calculate the portion of exemption:
Exempt Capital Gains: 4,39,79,100 * (3,00,00,000/5,00,00,000)
Exempt Capital Gains: Rs 2,63,87,460
The taxable capital gains = 4,39,79,100 - 2,63,87,460 = Rs 1,75,91,64.
Note: From April 1, 2024, the maximum deduction available under section 54F is Rs 10 crore. This limit came into effect from April 1, 2024, but was initially introduced in the Union Budget 2023.
What is the Difference Between Section 54 and 54F?
Let us now understand the differences between sections 54 and 54F of the Income Tax Act.
| Basis of Difference | Section 54F | Section 54 |
|---|---|---|
| Eligible Capital Asset | Tax exemptions are applicable on the sale of any capital asset other than residential property. | Tax exemptions are available on the sale of a residential property. |
| Amount of Exemption | Full or Partial Exemption allowed. | To the extent of long-term capital gain invested. |
| Reinvestment Requirement | Entire sale proceeds must be reinvested. | The entire capital gains must be reinvested. |
| No. of properties eligible for exemption. | NA | One-time exemptions are available for investments in two provinces, provided the gains are less than Rs 2 crore. |
What is the Capital Gains Account Scheme (CGAS)?
This scheme was introduced by the government of India in 1988 under the Income Tax Act to help the concerned taxpayers save on capital gains. Here's how CGAS works:
A taxpayer who wants to sell an asset and claim a tax exemption under either Section 54 or 54F can use this account scheme. The taxpayer can deposit the money from selling the original assets into the CGAS account until they are looking to purchase or construct a new residential house.
The Capital gains account works like a fixed deposit, providing the taxpayer with some extra time to realize the capital gains into a new residential property. The capital gains account should be opened with an authorized bank in India, and the amount deposited in such an account can only be used either to build or purchase a new house within a specific time frame.
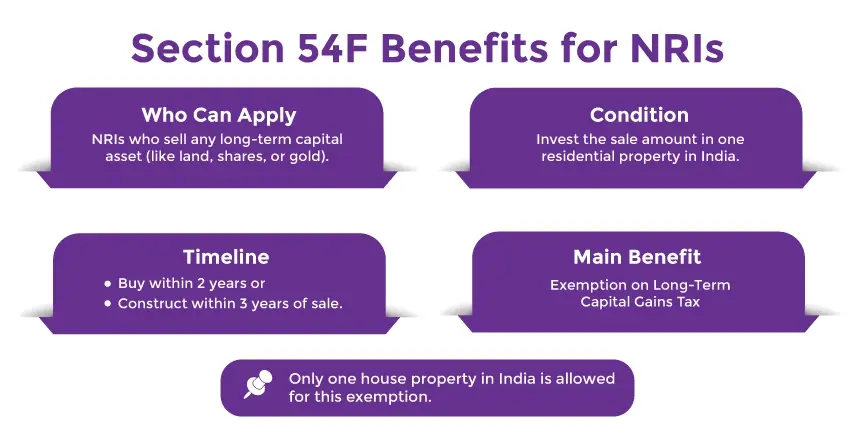
Benefits of Section 54F of the Income Tax Act?
Section 54F brings in a lot of benefits for Indian residents and non-indian residents (NRIs) like:
Aids in Saving Tax: As the section 54F allows the concerned taxpayer to claim an exemption on long-term capital gains, which results in avoiding taxes.
Facilitates Housing Investment: Since the tax exemption under this section is only granted when individuals invest their sale proceeds in a residential property, which results in support for the individual and the housing sector.
Applies to a Varied Range of Assets: Unlike section 54, section 54F is not just limited to the sale of residential property; instead, it includes other long-term capital assets, like land, shares, and more.
Applicable to NRIs: Non-resident Indians (NRIs) can also claim the benefit under section 54F, given that the reinvestment is made in a residential property located in India.
Aids in Long-Term Financial Planning: This section encourages taxpayers to invest their long-term capital gains in more stable assets, such as real estate and housing, which serve as a future asset or a residence to live in.
How Can Savetaxs Help with Section 54F?
We at Savetax provide a varied range of tax services, including NRI income tax consultancy, ITR filing, repatriation, and more. We have a team of experts with over 30 years of combined experience providing NRIs with personalized NRI tax planning to optimize the capital gain tax liability of each client while ensuring they deserve every exemption possible.
Savetaxs boasts a staggering client base of thousands of NRIs like you, being a beacon of the kind of services we offer. So, what's stopping you? We are available 24/7 across all time zones to provide our clients with the best long-term capital gain tax for NRI advice possible.

Mr. Ritesh has 20 years of experience in taxation, accounting, business planning, organizational structuring, international trade financing, acquisitions, legal and secretarial services, MIS development, and a host of other areas. Mr Jain is a powerhouse of all things taxation.
Want to read more? Explore Blogs
Frequently Asked Questions
No matter what your source of income is, we've got you covered. There’s a plan for everybody!



_1760618042.webp)
_1766742512.webp)