- Types of Properties NRIs can Sell
- Documents Require For NRI Selling Property In India
- Tax Implications For NRIs Selling Property In India
- Tax Deducted At Source (TDS) For NRI Property Sale
- How To Repatriate Sale Proceeds Abroad
- Tax Exemption On Capital Gains Available To NRIs
- Power of Attorney (PoA) for NRIs Selling Property
- Legal & Practical Tips For NRIs Selling Property In India
- Get Expert Help On NRI Selling Property In India
NRI selling property in India is a complex process, but with the proper understanding and professional guidance, it's a win-win. There is no doubt that the growing Indian real estate market is a lucrative investment opportunity for NRIs, offering strong rental yields and capital appreciation.
NRIs choose to sell their property in India for various reasons, such as diversifying their investment portfolio, meeting financial needs abroad, repatriating funds, and more.
In this guide, we will discuss the key steps, strategies, and actions NRIs must take to liquidate their real estate assets effectively.
- While selling property, NRIs must adhere to the regulations of the Reserve Bank of India and the Foreign Exchange Management Act for all the transactions and fund repartitions.
- NRIs can sell commercial and residential properties in India. However, they face restrictions while selling farmhouse, plantation, priority, or agricultural land to other NRIs and PIOs.
- NRIs can appoint a notarized power of attorney (PoA) to handle the entire selling process on their behalf.
- During the property sale, an Aadhaar card is not mandatory, but it simplifies transactions. However, it is important to have a PAN card to claim the TDS refund.
Types of Properties NRIs can Sell
Non-resident Indians (NRIs) are permitted to own and sell the following types of properties in India.
- Commercial property: this includes shops, warehouses, offices, and similar properties.
- Residential Property: this includes apartments, villas, houses, and similar properties.
Please note that as an NRI, you are not permitted to invest in plantation properties, agricultural lands, farmhouses, and more. However, if you happen to inherit any such property, then it can be sold only to an Indian resident and not to NRIs/PIOs.

Documents Require For NRI Selling Property In India
The following are the documents that NRIs require to sell property in India:
Passport: Any non-resident Indian who wishes to sell a property in India must hold a valid passport. This will serve as their proof of identity.
Similarly, for PIOs and Overseas citizens of India, a passport will serve the same purpose.
PAN Card: Having a PAN card is important for NRIs with property in India. As for the process, you might be required to apply for a tax exemption certificate after the sale of property.
If you don't have a PAN Card, please apply for it well in advance of the property sale process.
Power of Attorney: For NRIs who can't be physically present in India to sell their properties, they can grant a Power of Attorney (PoA) to a close relative, family member, or friend to complete the transactions on their behalf.
Any individual with the power of attorney has the authority to sign official documents and other agreements on your behalf. The PoA can be specific or general about he rights the person representing you can exercise.
Tax Returns: When an NRI holds a property for a certain period and earns income from renting it, the transaction becomes taxable. The tax returns for the entire property ownership must be prepared.
Address Proof: During the sale of a property, the NRI must provide documents supporting both the Indian and overseas addresses. The documents include a ration card, electricity bills, telephone bills, life insurance policies, political settlements, and more.
Sale Deed: A sale deed is a legal agreement that serves as the primary proof of property ownership.
Documents From The Society: These documents are needed when the property to be sold is in a particular society. These documents inform the buyer that the seller has no outstanding liens to the city.
Encumbrance Certificate: This certifcate ensures that the buyer of the property or land they are about to purchase has no dues to any legal authority. An encumbrance certificate is important when selling an apartment, house, or even land.
Additionally, apart from these documents, if an NRI can provide property tax receipts from over the years, that would be helpful.
Tax Implications For NRIs Selling Property In India
Whenever a nonresident Indian NRI sells a property in India, the property generated is taxed as capital gains. The nature of the gains depends solely on how long the priority has been held.
The holding period of property is either long-term or short-term:
Long-term capital Gains (LTCG): When an NRI sells the property after holding it for more than two years from the date of purchase, then the gains generated from that property sale will be treated as long-term capital gains.
Short-term Capital Gains (STCG): When an NRI sells the property within two years from the date of purchase, the gains arising from such property are treated as short-term capital gains (STCG).
Applicable Tax Rates For NRIs on Property Sale
NRI capital gain for property sale applicable tax rates are.
Short-term capital gain (STCG): When the property is sold within 2 years of purchase, the gains are treated as STCG and taxed at the applicable slab rates.
Long-term capital Gains (LTCG): When the property is sold after two years from the date of purchase, the gains are considered long-term capital gains and are taxed as follows.
- Properties purchased before 23 July 2024: The gains are taxed at 20% with the indexation benefit.
- Property purchases on or after 23 July 2024: The gains are taxed at 12.5% without the indexation benefit.
Tax Deducted At Source (TDS) For NRI Property Sale
Whenever a property is purchased or sold in India, the TDS is deducted. It is the buyer's responsibility to deduct the TDS amount when paying the seller for the property. The deducted amount by the buyer must then be deposited with the Income Tax Department.
For NRIs selling property in India, the same rule applies. Let us understand the applicable TDS rates for NRI property sales under LTCG and STCG.
The Applicable TDS rates on NRI property Sales.
- If the property is sold within two years, it constitutes short-term capital gains: The TDS on sale of property is 30% of the sale consideration.
- If the property is sold after 2 years, it constitutes long-term capital gains: the TDS rate is 20% plus cess and surcharge.
Unlike Indian resident sellers, where the TDS deduction rate is 1% under section 194-IA, the TDS on the sale of property by NRIs is higher. This is because the TDS is deducted from the capital gains tax liability.
The TDS is deducted when the buyer is making the payment to the seller.
How To Claim NRI TDS On Property Sale Refund
In case of NRIs claiming a refund of excess tax deducted at source (TDS), you have to file an Income tax refund. This is the only way to recover the extra tax deducted, even if your total income is below the taxable limit.
Here's how to claim the NRITDS Refund.
Step 1: Gather the necessary documents.
Please keep the following documents in order, as they will help you claim the TDS refund.
- Permanent Account Number: A valid PAN Card is mandatory.
- Form 26AS: You must download this form from he official income tax website. Through this form, you can verify that the TDS deducted has been credited against yur PAN.
- Form 16A: As a seller, you must get this TDS certificate from the party that deducted the TDS, such as your bank or tranant.
- NRO Bank Account: As an NRI seller, ensure your NRO account is pre-validated on the eflining portal, as the refund will be credited to it.
- Investment and Income roofs: These include your property sale deed, interest certificates, rent agreements, and so on.
- Tax Residency Certificate: A TRC is needed if you plan to claim benefits under the double taxation avoidance agreement.
Step 2: Apply for a lower TDS Rate (Optional)
To avoid excessive TDS being deducted in the first place, you must apply for a lower or NIL TDS certificate. To apply for NE, you must submit Form 13 to the Income Tax Assessing Officer (AO).
The AO will review your application and, if satisfied, issue a certificate that will allow the deductors to withhold tax at either a lower or zero rate for future transactions.
Step 3. File Your Income Tax Return (ITR)
To file the income tax return, register on the portal by logging in to the income tax e-filing portal at incometax.gov.in.
Choose the appropriate form for NRIs: use Form ITR-2 if you do not have business income in India, or Form ITR-3 if you do.
Accurately report all income earned in India and the total tax deducted at source as per your Form 26AS.
Lastly, file the return and e-verify it.
Step 4. Receive the refund
After processing your income tax return, the ITD will credit your excess tax to your designated NRO bank account. Now this process can take a few weeks.
How To Repatriate Sale Proceeds Abroad
To repatriate the funds from the sale proceeds abroad, follow the steps below.
Step 1: Deposit the proceeds
Deposit the sale proceeds of the property in your NRO bank account.
Step 2: Gather all the necessary documents
Keep the following documents in order:
- Form 15CA
- Form 15CB
- Repatriation Application Form
- Sale Deed
- Proof of Ownership
- Bank Statements
- PAN Card
- Proof of Identity
- Encumbrance Certificate
- Documents of Inherited Property (If applicable)
Step 3: Submit the documents to the Bank
Ultimately, the gathered and recorded documents are submitted to your authorized bank. The bank will review the documents and then process the funds transfer to your foreign bank account.
Step 4: The Limits and Rules
As an NRI, you can repatriate up to one million USD in a financial year from your NRO account.
In case of repatriation of additional funds, you can seek approval from the Reserve Bank of India.
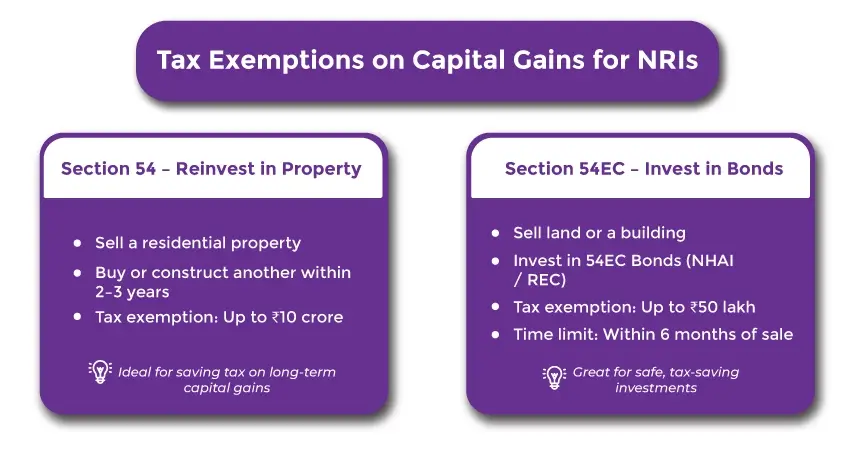
Tax Exemption On Capital Gains Available To NRIs
NRIs can claim tax exemptions under Sections 54 and 54EC on long-term capital gains from the sale of residential property in India.
Exemption Under Section 54 Of the Income Tax Act
Section 54 of the Income Tax Act provides an exemption from the long-term NRI capital gains tax if an individual plans to reinvest their capital gains in another residential property.
In terms of reinvesting, you can either purchase another residential property within two years or construct one within the time frame of three years from the date of sale. Tax exemption up to 10 crore can be claimed.
Doing so helps the taxpayer save taxes by reinvesting the proceeds in a new home, provided all the conditions under the Act are met.
Exemption Under Section 54EC Of The Income Tax Act
Whenever a long-term immovable asset, such as land, building, or both, is sold, the profits earned are taxable. However, the taxpayer can avoid or reduce the tax liability by claiming a tax exemption under section 54EC of the Income Tax Act.
Under this section, you invest the capital gains in the specified bonds notified by the central government within 6 months from the date of sale. Such bonds are also known as capital aid bonds or 54EC bonds, and investing in them allows the taxpayer to avoid paying taxes.
Power of Attorney (PoA) for NRIs Selling Property
Non-resident indian use a power of attorney to appoint an attorney or agent to help them sell their properties in India. NRIs do so because they find it challenging to be physically present in India.
A POA authorizes the holder to make decisions on behalf of the owner of the property. You can choose a close relative or a trusted legal professional to hold power of attorney for the NRI property sale.
Legal & Practical Tips For NRIs Selling Property In India
As an NRI, if you are selling a property in India, here are a few legal and practical tips to consider.
Verify the property's ownership: Before making any sales, please ensure that the property title is clearly stated and that the property is legally registered under your name. And if the property is inherited, please ensure that you have either a succession certificate or the will.
Please stay compliant with FEMA: During the process of selling your property, please ensure that you adhere to the guidelines of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Foregin Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
Tax obligations: As an NRI, understanding the indian tax implications regarding the capital gains tax is essential.
Professional Property Valuations: You must obtain a professional appraisal to determine the property's actual market value and avoid potential losses.
Get a NOC: When selling a property in a housing society, please ensure you obtain a no-objection certificate from the relevant authority.
Maintain records: You must keep all your transactions and communication records clearly stated.
Get Expert Help On NRI Selling Property In India
As aforementioned, selling a property in India as an NRI can be a tedious task, especially if you lack an understanding of the Indian real estate market and Indian taxation. Hence, it is advisable to seek the help of a professional with expertise in both Indian and foreign taxation and the Indian real estate market for NRIs.
Savetaxs is one such expert and the emerging name in the taxation industry for NRIs. When it comes to selling a property in India as an NRI, Savetax will help you with all documentation, including assisting with Form 15CA/15CB, obtaining lower TDS certificates, consultations on repatriation of funds, drafting a power of attorney, and more.
Our experts bring over 30 years of experience to the table, hence you can rest assured that they will help you navigate the complexities of NRI property transactions and more.
So, if you are an NRI planning to sell a property in India, connect with Savetaxs today and enjoy the benefits we bring for you. Savetaxs is serving its clients 24/7 across all time zones. Get in touch with us, and our experts will help you with a personalized sales strategy for your property.
Note: This guide is for information purposes only. The views expressed in this guide are personal and do not constitute the views of Savetaxs. Savetaxs or the author will not be responsible for any direct or indirect loss incurred by the reader for taking any decision based on the information or the contents. It is advisable to consult either a CA, CS, CPA or a professional tax expert from the Savetaxs team, as they are familiar with the current regulations and help you make accurate decisions and maintain accuracy throughout the whole process.

Mr Shaw brings 8 years of experience in auditing and taxation. He has a deep understanding of disciplinary regulations and delivers comprehensive auditing services to businesses and individuals. From financial auditing to tax planning, risk assessment, and financial reporting. Mr Shaw's expertise is impeccable.
- Everything You Need to Know About Form 15CA and 15CB of Income Tax
- Can NRIs Change Their Tax Regime While Filing Their ITR In India?
- Tax Guide for Working from India for a US Company After Expire of H-1B Visa
- How NRIs can e-verify IT Return From Abroad?
- Inheritance Tax On NRI (Non-Resident Indians) In India
- Section 80C of Income Tax Act - 80C Deduction List
- Your Complete Guide on TCS on Foreign Remittance
- What is Section 54 and Section 54F for NRIs?
- Section 9 Of The Income Tax Act
- A Comprehensive Guide to the Annual Information Statement
- A Guide on the Types of TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) in India
- Complete Guide On What is ITR, Documents Required, ITR Forms & Why To File
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 - FEMA
- Income Tax Form 13 For NRIs - Lower or Non Deduction
- Form 27Q Simplified For NRIs- TDS Return on Payments
Want to read more? Explore Blogs
Frequently Asked Questions
No matter what your source of income is, we've got you covered. There’s a plan for everybody!
_1752921287.webp)
_1767080655.webp)




_1767339016.png)
_1768807342.webp)



_1760618042.webp)






