Looking for a simple way to claim tax benefits on home loan interest, HRA, Section 80C investments, and more? Then you must know about Form 12BB - a standardized tax declaration form introduced on 1 June 2016 by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT). Since its launch, it has become a crucial document for salaried employees as well as Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) earning income in India.
Under Section 80C alone, NRIs can save up to INR 46,800 using the correct declarations in Form 12BB.
For both residents and NRIs, Form 12BB is not optional—it is essential for claiming tax deductions and ensuring accurate TDS calculation. By declaring eligible investments, expenses, and tax-saving instruments, you can claim deductions up to INR 1,50,000 under Section 80C along with other allowances, including HRA, LTA, Section 24(b), and more.
If you are an NRI with income taxable in India, this guide will help you understand why Form 12BB for NRIs is important and how to use it effectively.
What is Form 12BB?
Form 12BB is a unified tax declaration form for salaried individuals, introduced by the CBDT to standardize investment and deduction declarations that employees submit to employers.
Before 2016, employers used inconsistent formats for tax declarations. Form 12BB replaced all of them with one universal format.
Who Should Submit Form 12BB?
- Salaried individuals
- Salaried NRIs earning income in India
- Employees claiming tax benefits like HRA, LTA, 80C, 80D, home loan interest, etc.
Where to Submit?
You do not submit Form 12BB to the Income Tax Department. It must be submitted directly to your employer, usually between January and February every year.
Form 12BB PDF Download
Form 12BB Sample
For NRIs in particular, this helps streamline tax planning and prevent unnecessary TDS deductions.
Role of Form 12BB in NRI Tax Planning
If you are an NRI receiving salary income in India, Form 12BB acts as your NRI tax declaration form. It links your eligible tax-saving investments to the tax benefits your employer should consider when calculating monthly TDS.
Why Form 12BB Matters for NRIs
NRIs with salary income in India can use Form 12BB as a tax shield. However, without giving this form to your company or employer, you cannot get tax relief from the deducted TDS on your salary. Based on the declarations you made in Form 12BB, your employer calculates your monthly applicable tax deduction. Through this form, you can streamline your tax planning in the following ways:
- Helps claim key tax deductions regardless of residency status
- Forms the basis for employer-side TDS calculation
- Offers a uniform declaration process
- Prevents errors, over-deduction, and tax mismatches
Components of Form 12BB Relevant to NRI Tax Planning
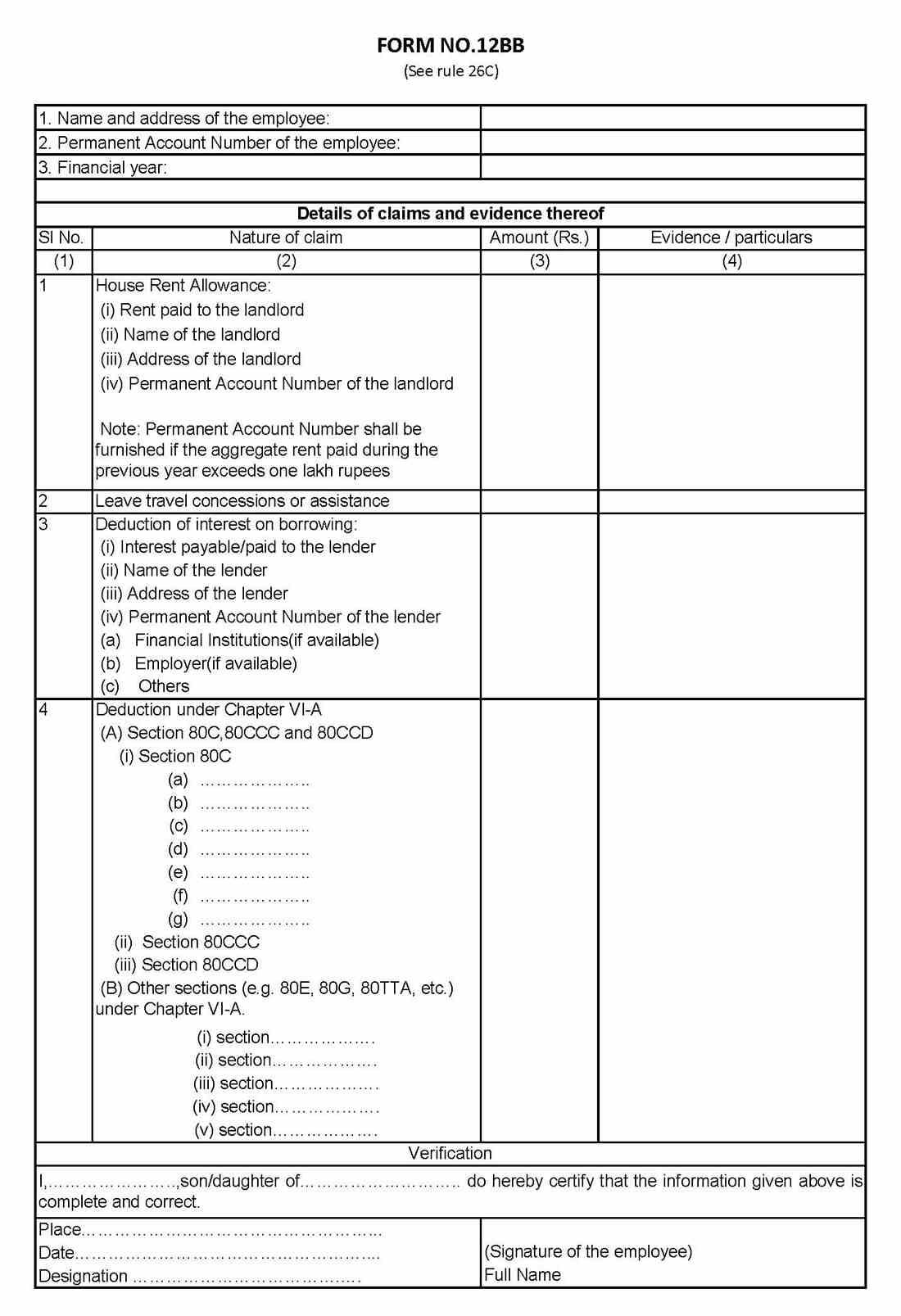
Form 12BB includes the following details:
Part I: Personal Details
- Name
- Current address
- PAN number
- Financial year
Part II: Details of Claims and Evidence
1. House rent allowance
If HRA is included in your salary, you must declare:
- Rent paid
- Landlord’s name & address
- Landlord’s PAN (mandatory if rent > INR 1,00,000 yearly)
- Proof: rent receipts or rental agreement
Important Notes:
- If HRA is not part of your CTC, claim deduction under Section 80GG.
- Cannot claim HRA if you are living in your own house.
- If living with parents, rent paid must show as rental income in their ITR.
- Avoid submitting fake rent receipts - this leads to penalties.
2. Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
LTA is one of the few allowances that offer tax-exempt domestic travel.
Eligibility
- Must be included in the salary structure
- Applicable for: self, spouse, dependent children, parents, and siblings
Key Rules
- Only domestic travel is allowed.
- Twice in a four-year block (Current block: 2022–2025)
- Unused LTA of one cycle can be carried forward to the next year
- Travel proofs required: flight/train tickets, boarding passes, or invoices
Accommodation expenses are not exempt.
3. Home Loan Interest Deduction (Section 24b)
NRIs can claim interest deduction on home loans taken for:
- Purchase
- Construction
- Renovation
- Repair
Details Needed in Form 12BB
- Interest amount paid/payable
- Lender’s name
- Lender’s address
- Lender’s PAN/Aadhaar
Tax Benefits for NRIs
-
Interest deduction up to INR 2,00,000 for self-occupied or let-out properties
-
Principal repayment under Section 80C up to INR 1,50,000
-
Additional benefits:
-
Section 80EE: Extra INR 50,000 for first-time home buyers (old eligibility criteria apply)
-
Section 80EEA: Additional INR 1,50,000 (specific conditions apply; cannot be claimed if 80EE is used)
-
Proof Required
- Interest certificate from bank/NBFC
- Possession or completion certificate
- Self-declaration whether the property is self-occupied or rented

Disclaimer: This image is for educational purposes only.
4. Deductions Under Chapter VI-A
This is the final section of Form 12BB and contains the maximum tax deduction available under Chapter VI-A of the Income Tax Act. It includes several sections, such as 80C investments, Section 80G donations, and more. See the table below for the available deductions.
| Sections | Conditions to Avail | Maximum Deduction |
|---|---|---|
| 80C | Tax deduction for expenses and investments such as Public Provident Fund (PPF), life insurance premiums, National Savings Certificates (NSC), Employee Provident Fund (EPF), payment of tuition fees, and principal repayment of a housing loan. | INR 1,50,000 |
| 80CCC | Tax deductions for employees' contributions to pension funds offered by the private and public sectors. | INR 1,50,000 |
| 80CCD | An additional deduction is available for contributions of employees to the National Pension System (NPS) | INR 2,00,000 |
| 80D | Tax deduction available for medical insurance premiums for self, parents, spouse, and dependent children. | INR 25,000, which can be increased to INR 50,000 if parents are senior citizens. |
| 80E | Deduction for paid interest on the loan taken for higher studies. | Available for 8 years |
| 80G | Deduction for donations given to political parties, charitable organizations, and trusts. | Based on the donation type, the limit varies |
| 80TTA | Tax deductions for earned interest on savings accounts. | INR 10,000 |
Part III: Verification
The final section requires:
- Your name
- Parent’s name
- Place (city)
- Date
- Signature
This verifies that all declarations made are accurate and supported by documents.
Important Considerations for NRIs
- Submitting Form 12BB does not guarantee tax benefits; you must submit supporting documentation.
- You cannot submit Form 12BB to the IT Department - it goes only to your employer.
- If you change jobs, you must submit Form 12BB to each employer separately.
- Incorrect disclosures may lead to penalties or additional tax liability.
Things to Check Before Filing Form 12BB
Before submitting your NRI tax declaration form, ensure:
- HRA/LTA are part of your CTC
- Rent receipts or agreements are ready
- Loan repayment schedule & interest certificate are available
- All investment receipts under 80C are collected
- Proofs for donations, tuition fees, and other deductions are kept handy
How to Fill Form 12BB?
1. Enter Personal Details: Provide your name, address, PAN, and financial year.
2. Declare HRA Claims: Enter the rent details and landlord details, and attach receipts.
3. Declare LTA Claims: Attach travel proofs for domestic travel.
4. Declare Home Loan Interest: Provide lender details and interest certificate.
5. Declare Deductions under Chapter VI-A: Submit proofs for 80C, 80D, 80G, 80E, etc.
6. Verify & Sign: Sign the form confirming all details are accurate.
Final Thoughts
Whether you are an Indian resident or an NRI, it is essential to manage your tax obligations in India. In this, Form 12BB is a vital component to save tax on your investments. Through this blog, we have provided you with all the information about this form and how you can claim tax deductions through this. Moreover, if you need more guidance on Form 12BB or are facing issues in filing out this form, consider taking help from a tax expert like Savetaxs. We have a team of professionals who assist you in solving your tax-related queries and help you in filing your ITR on time. So connect with us now.
Note: This guide is for informational purposes only. The views expressed in this guide are personal and do not constitute the views of Savetaxs. Savetaxs or the author will not be responsible for any direct or indirect loss incurred by the reader for taking any decision based on the information or the contents. It is advisable to consult with either a Chartered Accountant (CA) or a professional Company Secretary (CS) from the Savetaxs team, as they are familiar with the current regulations and help you make accurate decisions and maintain accuracy throughout the whole process.

Mr. Ritesh has 20 years of experience in taxation, accounting, business planning, organizational structuring, international trade financing, acquisitions, legal and secretarial services, MIS development, and a host of other areas. Mr Jain is a powerhouse of all things taxation.
- A Guide on the Types of TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) in India
- Section 80TTA of Income Tax Act – All about Claiming Deduction on Interest
- Section 80CCC: Deduction on Pension Fund Contributions
- Section 197 Certificate or Lower Deduction Certificate for NRIs and Indians?
- Your Complete Guide for Section 80D of the Income Tax Act
- What is House Rent Allowance: HRA Exemption, Tax Deduction, Rules & Regulations
- Understanding All About Income Tax Clearance Certificate
- Section 115H Of Income Tax Act: Benefits & Provisions
- Section 80CCD Of Income Tax Act: NRIs Tax Savings Guide
Want to read more? Explore Blogs
Frequently Asked Questions
No matter what your source of income is, we've got you covered. There’s a plan for everybody!




_1767077669.webp)

_1756467732.webp)

_1767604193.webp)









_1752921287.webp)