- What is Form 1099-B: Proceeds from Broker and Barter Exchange Transactions?
- What Information is Included on the IRS Form 1099-B?
- Who Needs to File Form 1099-B?
- How is Form 1099-B Used?
- Barter Exchanges
- Filing Instructions for Form 1099-B
- Short-Term and Long-Term Gains
- Related Tax Forms to Know
- How Do You Read the Form 1099-B?
- Do I Need to Report 1099-B On My Taxes?
- Is 1099-B Earned Income?
- To Conclude
Form 1099-B reports transaction proceeds acquired from broker transactions or bartering networks. You will get a Form 1099-B from each broker if you have sold stocks, bonds, or any other security by the 17th of February. This tax document contains several information that may be essential.
It includes the item description, purchase, and sale dates, and any federal tax withheld. In this blog, we will walk you through everything you need to know about Form 1099-B. Also, you will learn how to compute capital gains or losses easily through Form 1099-B.
- Brokers and barter exchanges use Form 1099-B to report gains or losses to the IRS for the tax year.
- It can include gains or losses acquired from selling stocks, bonds, derivatives, or other securities through a broker, and for barter exchange transactions.
- It also reports the fair market value of goods and services acquired through barter exchanges, which is usually treated as taxable income.
- The information from Form 1099-B is transferred to Form 8949 by the taxpayer to compute gains and losses. Later, the details are recorded on Schedule D. Generally, gains are taxable, while losses can offset gains or lower taxable income.
- Form 1099-B contains details like the sold item's description, purchase and sale date, cost of acquisition, sale gains, and any federal tax withheld by the broker.
- You must receive a copy of Form 1099-B from your broker by the 17th of February every year to include it in your tax returns.
What is Form 1099-B: Proceeds from Broker and Barter Exchange Transactions?
Brokers and barter exchanges use Form 1099-B to report taxpayers' gains and losses every year. It enables the taxpayers to compute gains and losses through Form 8949. Also, it is required to complete Schedule D on their tax returns.
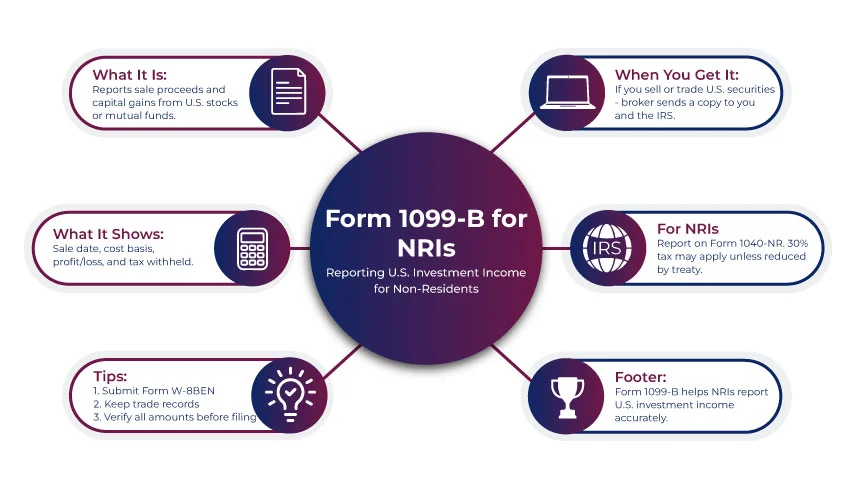
What Information is Included on the IRS Form 1099-B?
Generally, a 1099-B form reports information related to securities or property involved in a transaction, which is handled by a broker. The information may include the following:
- The date when you sold it
- The amount you paid to acquire it
- The date when you bought or acquired it.
- How much did you get in return when you sold it
- Whether your broker withheld any federal tax.
- a brief description about the sold item, like "100 shares of ABC Co.".
Who Needs to File Form 1099-B?
A broker sends a 1099-B form to the IRS as well as each customer who sold investments during the year. It records a taxpayer's gains or losses.
For example, suppose you sold a few stocks last year through which you acquired $10,000 as sale proceeds. So, the broker will report this $10,000 figure to the IRS through a 1099-B form and through you as a report of taxable capital gain.
Additionally, companies taking part in bartering may also have to file this form to report changes made in a corporation's capital structure or stock control.
How is Form 1099-B Used?
Form 1099-B helps you in dealing with capital gains and losses on your tax return. Generally, when you sell something and the sale proceeds are more than it cost you to acquire it. In such a case, the profit will be treated as capital gains, and it may be subject to taxation.
On the contrary, if you sell something for less than the amount you paid to acquire it, then you may have a capital loss. You might be allowed to use this to lower your taxable capital gains or any other income.
- Capital gains taxes are paid with your income tax return, usually using Schedule D.
- If required, you can use the information from Form 1099-B to complete Schedule D and Form 8949.
Barter Exchanges
Form 1099-B is also used to report barter exchange transactions. A barter exchange is basically a network of people or companies who decide to trade property or services with one another without accepting any payment in currency.
Box 13 of the form is used by barter exchanges to report the fair market value of goods and services received by a member of the exchange throughout a year. Generally, value acquired through a barter exchange is treated as income and may be subject to taxation.
Filing Instructions for Form 1099-B
A brokerage or barter exchange needs to file a separate 1099-B for individual transactions related to sales. It includes short sales of different securities and contracts.
Commissions are not reported on this form as they do not apply to these transactions. The form shows the cash received and the fair market value (FMV) of goods or services acquired or any trade credits received.
During the bartering activity, you may receive a gain receipt that may need to be reported. Reportable gains can be in any form, such as cash, property, or stock.
A broker or barter exchange is liable to report each transaction on a separate Form 1099-B. This doesn't include regulated futures, foreign currency, or Section 1256 option contracts.
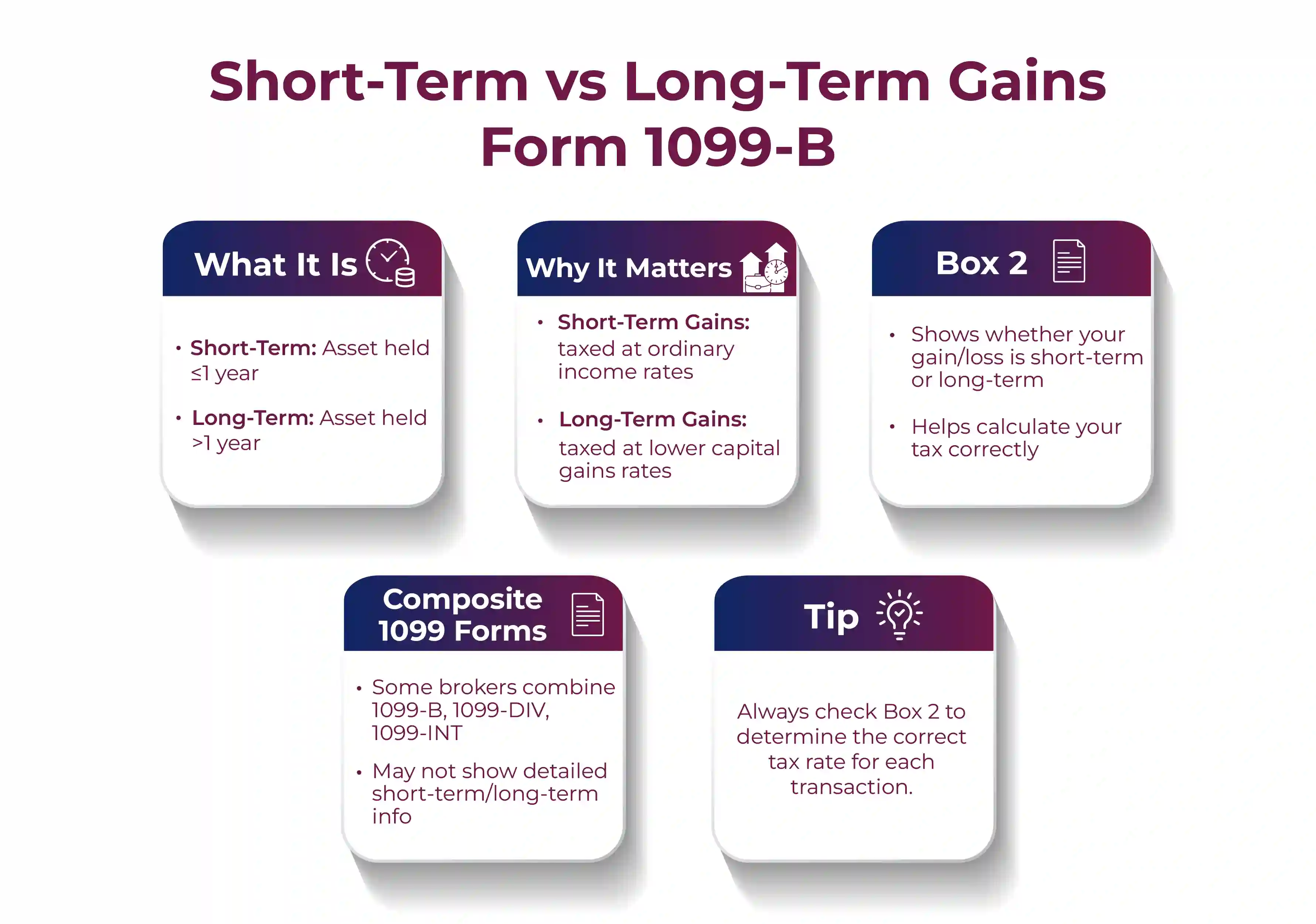
Short-Term and Long-Term Gains
Box 2 of the form indicates whether the gain or loss involved is either short-term or long-term.
Typically,
- In case you held an asset for a year or less before selling it, such as a stock. Then, any gain or loss acquired from selling it will be treated as short-term in most cases.
- On the other hand, if you owned the asset for more than a year. Then, you would normally have a long-term gain.
- Understanding this difference is essential as tax rates applicable to long-term gains can be significantly lower than those on short-term gains.
Some brokerage companies may issue a "Composite 1099 Form" that substitutes a few other 1099 forms, such as:
- 1099-B
- 1099-DIV
- 1099-INT
The individual sections of the composite forms don't include all the information that can be accessed from a standard 1099 form. Such as the check boxes for short-term and long-term transactions that are available on the standard 1099-B form.
Rather, several composite forms simply group the various transaction types that help you easily determine whether they are short-term or long-term.
Related Tax Forms to Know
You need to file Schedule D if you received a 1099-B form. Schedule D is where you record your gains and losses for the year. Form 8949, Sales and Other Dispositions of Capital Assets, is used to document the transaction details.
How Do You Read the Form 1099-B?
Form 1099-B contains information about the issuer and the taxpayer. It also contains a description related to the sold property, the acquisition date, the sale date and price, the original price, and any deductions that may apply. Other information includes any federal tax withheld, gains or losses incurred, and any state tax withholdings.
Do I Need to Report 1099-B On My Taxes?
Although you don't need to provide the actual Form 10990B to the IRS along with your tax return. However, you need to include the information mentioned on it on Form 8949 and submit that along with Schedule D. Later, you will use it to record your aggregates for all transactions shown on Form 8949.
Is 1099-B Earned Income?
No, 1099-B reports capital gains and losses. A capital gain or loss arises from selling an asset that you own. It includes a stock, stock option, or bond. On the other hand, earned income is the income that you get from your employment.
To Conclude
Brokers and barter issues Form 1099-B to report to the IRS and the client about the taxpayer's capital gains and losses. Although it is not included with the tax return, the data on Form 1099-B must be transferred to Form 8949. Later, this information is used to compute gains and losses, which are reported on Schedule D and provided with their tax return.
Furthermore, if you are facing any issues with understanding Form 1099-B or any other tax-related issues, connect with Savetaxs. Our team of experts will provide tailored assistance as per your situation. They will ensure to guide you from the start to the end of the process to resolve all your tax queries. Contact us today and experience expertise at your fingertips.
Note: This guide is for information purposes only. The views expressed in this guide are personal and do not constitute the views of Savetaxs. Savetaxs or the author will not be responsible for any direct or indirect loss incurred by the reader for taking any decision based on the information or the contents. It is advisable to consult either a CA, CS, CPA or a professional tax expert from the Savetaxs team, as they are familiar with the current regulations and help you make accurate decisions and maintain accuracy throughout the whole process.

Miss Sanskriti is a certified Tax Expert. She has her expertise in US GAAP, Taxation, SOX, IRS, Accounting, and Auditing standards. Miss Saxena is an intellectual blend of a high-end auditor, tax consultant, and accountant
- What is IRS Form 1099-C: Cancellation of Debt
- What is a 1099-G Tax Form?
- 1099 Form: Overview, Types, Uses, and Who Receives It.
- Form W-9: Who Can File And How to File It
- Form 1099-NEC: Purpose and Requirement
- IRS Form 1099-Q: Payments from Qualified Education Programs
- IRS Form 1099-INT: What It Is & Who Needs to File It?
- Understanding the Purpose of IRS Form 1099-MISC
- What Is The Difference Between a 1099 and a W-2 Tax Forms
- What is IRS Form 1099-A?
Want to read more? Explore Blogs
Frequently Asked Questions
No matter what your source of income is, we've got you covered. There’s a plan for everybody!
_1756467732.webp)



_1766492717.png)






_1752921287.webp)


_1760618042.webp)
_1767604193.webp)