An NRI must understand how US Social Security benefits are taxed in India, particularly those who are seeking to return to India and change into a new residency status. In this blog, we will walk you through everything you must know about the taxation of US Social Security benefits for returning NRIs. Additionally, we will learn about the India-US DTAA and effective tax strategies to help you stay compliant.
- Your taxability in India is determined based on your residency status under the Indian Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Your US social security income is generally not taxable in India under the NR or RNOR status.
- If the social security benefit amount is credited directly into an Indian bank account, it will be taxed in India.
- Utilize ITR-2 or ITR-3 to report US Social Security benefit income.
How Does Residency Status Impact Taxation?
Your tax liability is determined based on your residential status in India under the Indian Income Tax Act, 1961. The three primary categories of residency are as follows:
Resident and Ordinarily Resident (ROR)
For individuals with ROR status, global income, including US Social Security benefits, is taxable in India under the "Income from Other Sources" category. There are no specific tax exemptions for social security benefits under the Indian tax law, meaning the entire amount will be taxed.
Non-Resident (NR) and Resident but Not Ordinarily Resident (RNOR)
- Tax-Exempt in India: Under the NR or RNOR status, your US Social Security Income is generally not subject to taxation in India, provided it's acquired outside India.
- Not Liable for Reporting: You don't need to report the income held in US accounts in your Indian tax filings.
Some Main Exceptions
If the amount for social security benefits is credited directly into an Indian bank account, like NRE, NRO, or resident savings. Then, the amount becomes taxable in India. You must plan the receipt mode to prevent any unintended tax liabilities
India-US DTAA Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement
Under the India-US DTAA, taxpayers can avail relief from a significant tax amount:
- Residency Certificate: The DTAA's "tiebreaker rules" can be used by dual residents to determine their residency. Aligning residency with the US under the DTAA will help you ensure that the benefits remain tax-free in India.
- Exclusive US Taxation for Social Security: Under Article 20(2) of the DTAA, US Social Security benefits received by either Indian residents or US citizens will be taxed only in the United States.
Key Strategies for NRI Receiving US Social Security Income
If you are an NRI receiving US Social Security income, here are some strategies that you must consider:
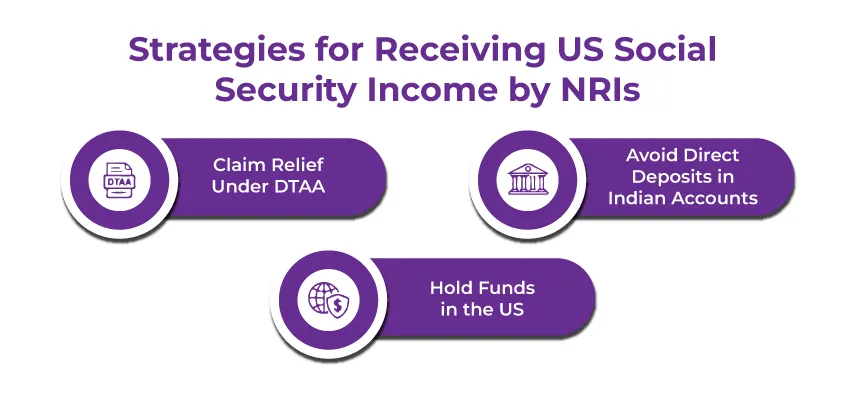
- Claim Relief Under DTAA: Ensure accurate reporting under DTAA provisions to reduce your tax liability.
- Avoid Direct Deposits in Indian Accounts: Benefits deposited directly into an NRO, NRE, or resident accounts become taxable in India.
- Hold Funds in the US: Keep your Social Security benefits in a US account and transfer funds to India when required. Remittances are not taxed in India.
How to File Tax Returns in India?
Follow the steps below if you are an ROR and need to report US Social Security benefits:
- Choose the Accurate ITR Form: Use ITR-2 or ITR-3, as ITR-1 doesn't support the reporting of foreign income.
- Fill Out the Main Schedules:
- Schedule OS: Report Social Security benefits and mention Article 20(2) of the DTAA to avail the exemptions.
- Schedule FSI: Report foreign income and taxes paid in the U.S. If the income is exempt under the DTAA, mention taxable income in India as "nil".
- Schedule EI: Under DTAA provisions, categorize exempt income.
The Bottom Line
If you are an NRI returning to India, you need to understand the tax implications of US Social Security benefits in India to stay compliant. You need to understand DTAA also to claim tax benefits and reduce a significant tax amount. Additionally, ensure to report the US social security benefits in the correct ITR form, which is ITR-2 or ITR-3.
Furthermore, if you need more assistance with navigating taxation for US social security benefits, understanding DTAA, or tax compliance for NRIs. Then, contact the experts at Savetaxs. We have a team of experts with years of experience in this field. They will offer personalized guidance to ensure you stay compliant while returning to India and make this transition easier. Contact us whenever needed, as we are working 24*7 across all time zones.
Note: This guide is for informational purposes only. The views expressed in this guide are personal and do not constitute the views of Savetaxs. Savetaxs or the author will not be responsible for any direct or indirect loss incurred by the reader for taking any decision based on the information or the contents. It is advisable to consult either a CA, CS, CPA, or a professional tax expert from the Savetaxs team, as they are familiar with the current regulations and help you make accurate decisions and maintain accuracy throughout the whole process.

Mr Varun is a tax expert with over 13 years of experience in US taxation, accounting, bookkeeping, and payroll. Mr Gupta has not prepared and reviewed over 5000 individual and corporate tax returns for CPA firms and businesses.
- Returning to India from Malaysia - A Guide for NRIs
- A Complete Guide for NRIs Returning to India from Australia
- A Guide for NRIs Returning to India from UAE
- USA Rental Income Tax for RORs in India
- Returning to India After Retirement: Tax Planning for NRIs
- A Guide for NRIs Returning to India from the UK
- Your Complete Guide for Tax Rules for NRIs Returning to India
- 529 Plan For NRIs Returning Back To India - Is It Still Worth It?
- A Complete Guide for NRIs Returning to India from the USA
- NRIs Returning from Canada to India- A Comprehensive Guide
Want to read more? Explore Blogs
Frequently Asked Questions
No matter what your source of income is, we've got you covered. There’s a plan for everybody!
NRIs can optimize the tax impact of social security benefits by:
- Timely filing
- Leveraging treaty benefits to reduce tax outgo.
- Planning receipt mode (e.g., credit to RFC or NRO accounts).