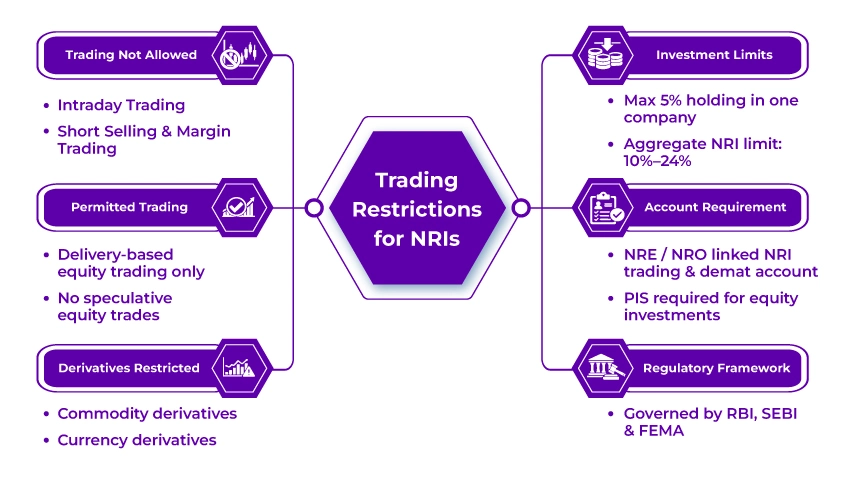
For NRIs investing in the Indian stock market from overseas, it has always remained exciting. However, NRIs face several trading restrictions in India, primarily being restricted from intraday trading, short selling, and trading in commodity/ currency derivatives.
These restrictions are imposed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to ensure fair markets and protect investors.
Furthermore, understanding these rules helps you avoid common mistakes and achieve the best returns. To help you out, this blog provides you with a clear understanding of the trading restrictions for NRIs in India. So read on and gather all the information.
- NRIs are not allowed to do intraday trading, short selling, or margin trading in India. Additionally, they are also restricted from using commodity/currency derivatives.
- NRIs need to open a specific bank account, i.e., NRE or NRO. Additionally, link it with their NRI trading and demat account under the Portfolio Investment Scheme (PIS) framework with an RBI-authorized bank.
- An NRI cannot hold a paid capital of more than 5% in any single Indian company.
- Before entering the trading market, NRIs need to submit copies of FEMA and FATCA declarations.
- Additionally, you need your Custodial Participant or CP code before starting F&O trading.
Trading Restrictions for NRIs in the Indian Stock Market
The table below showcases the trading restrictions for NRIs in the Indian stock market:
| Aspect | Trading Restrictions for NRIs |
|---|---|
| Equity Trading | Through NRI trading demat accounts, NRIs are only permitted for delivery-based equity trading. |
| Intraday & Margin Trading | Generally, NRIs are not allowed to do intraday trading and margin-based speculative trades. |
| Individual Holding Limit | NRIs in a single Indian company can hold a maximum of 5% of paid-up equity capital. |
| Aggregate NRI Holding Limit | With shareholder approval, capped at 10% which is extendable to 24%. |
| Currency & Commodity Derivatives | On Indian exchanges, it is generally not permitted for NRIs. |
| F&O Trading | With a custodian, F&O trading on a non-repatriable basis is allowed only via an NRO non-PIS account. |
| NRE-PIS Account Usage | On a repatriable basis, NRE-PIS account usage is restricted to delivery-based equity investments. |
| Regulatory Oversight | Governed by the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), RBI, and SEBI guidelines. |
This was all about the trading restrictions for NRIs. Moving ahead, now let's know the account and compliance requirements that NRIs need to follow while trading in India.
Account and Compliance Requirements for NRIs
Here are the account and compliance requirements that NRIs need to follow for trading in India:
- To route all transactions related to investments, NRIs need to have an NRE or NRO bank account.
- For holding and settling securities traded on Indian exchanges, it is mandatory to have an NRI demat account.
- NRIs should have an NRI trading account, which is tagged as:
- PIS Account: It is used for equity investment repartition through an NRE account.
- Non-PIS Account: It is used for F&O trading and delivery-based equity through an NRO account.
- To prescribe the limits of investment, banks need to report all PIS-linked trades to the RBI.
- Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance is mandatory. It includes identity verification, periodic updates, and overseas address proof.
- To disclose tax residency and details of overseas tax identification, it is vital to submit FATCA and CRS declarations.
- NRIs should create a clear documentation of the fund sources, specifically for frequent or large transactions.
- Individuals who move overseas for education or work and qualify as NRIs should convert their resident savings account and Demat account to NRI status.
- Further, you cannot use your resident demat or trading account without conversion after your residential status change, as it is not allowed. Additionally, you may also face legal issues for regulatory violations.
This was all about the account and compliance requirements that NRIs need to follow while trading in India. Moving further, let's know the tax and repatriation rules impacting NRI trading.
Tax and Repatriation Rules Affecting NRI Trading
NRIs are subject to specific tax and repatriation rules for trading in the Indian stock markets. These rules are generally governed by the Income Tax Act and FEMA. Additionally, the rules depend on the nature of the income and the used bank account type, i.e., NRE or NRO account.
Further, the income that is accrued or earned in India only for NRIs is liable to be taxed in India. Considering this, the table below showcases how capital gains from Indian securities are taxed:
| Investment Gain | Holding Period | Tax Rate (plus surcharge & cess) |
|---|---|---|
| Equity Shares/ Equity Mutual Funds | Short-term capital gain if held for less than 12 months | 15% |
| Equity Shares/ Equity Mutual Funds (annually) | Long-term capital gain if held for more than 12 months | 10% tax imposed on capital gains more than INR 1,00,000 |
| Debt Mutual Funds | Short-term capital gain if held for less than 36 months | As per applicable income tax slabs (up to 30%) |
| Debt Mutual Funds | Long-term capital gains if held for more than 36 months | 20% with indexation benefits |
| Derivatives (F&O) | Treated as business income | Taxed according to the applicable slab rates. |
| Dividends/ Interest DTAA | Not applicable | Taxed at 20% or 30% TDS, depending on your income sources and DTAA |
Additionally, TDS is mandatory for most NRI income in India. It is often deducted by the fund house or bank at the time of payment. In case the deducted TDS is more than the actual tax liability, NRIs can claim for refund when filing their ITR.
Further, let's know about the repatriation rules.
Repatriation Rules
Repatriation can be defined as the process of fund transfer from India to your resident country. The repatriation rules are governed by FEMA. Further, let's know about them.
NRE/ FCNR Accounts: Under these accounts, you can transfer both the principal invested amount (foreign currency source) and the earned interest/ capital gains. Without restriction, you can fully repatriate the whole amount.
NRO Accounts: Funds in an NRO account, generally for India-sourced income or non-repatriable investments, can be repatriated up to USD 1 million per financial year. Across all NRO accounts, this repatriation limit is cumulative. Additionally, it requires tax compliance and specific documentation, such as Form 15CA and Form 15CB, certified by a CA.
DTAA Benefits: With over 90 countries, India has signed a Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA). It helps NRIs to avoid paying taxes on the same income twice (once in India and once in the resident country). To claim the DTAA benefits, NRIs need to provide a Tax Residency Certificate and Form 10F.
These were the tax and repatriation rules that impact NRI trading. Moving ahead, let's know how to stay compliant and avoid mistakes in trading.
Connect with Savetaxs, and get help from financial experts for your NRI taxation in India, and stay compliant with the tax laws.
How NRIs Can Stay Compliant and Avoid Mistakes in Trading?
Here are some tips that help NRIs to stay compliant and avoid mistakes in trading:
- Open the correct trading account and choose a reputable broker. Additionally, specify to the broker whether you want F&O or equity delivery access. Provide all the requested documents, including your NRI PAN card and KYC form.
- If you opt for F&O trading through your broker, you need to appoint a custodian and get a CP code. Without the CP code, your orders will not proceed further.
- Do not try to do intraday equity trades, short selling, Sell-Today-Buy-Tomorrow (STBT)/ Buy-Today-Sell-Tomorrow (BTST) orders, or commodity/ currency trades. For equities, use a delivery-based approach.
- Check whether sovereign gold bonds (SGBs), certain mutual funds, or ETFs are available to you, specifically if you reside in the US or Canada.
- Be aware of the aggregate NRI investment and sectoral caps limits. Generally, these are enforced by brokerage platforms. However, having information about the helps you in better planning of your investment strategy.
- In case of your residential status change from an Indian resident to an NRI, inform your broker about this. It is mandatory to convert your resident account to an NRI account when you move overseas.
So, follow the above tips and stay compliant with the trading rules for NRIs.
Final Thoughts
Lastly, this was all about trading restrictions for NRIs in India. Trading in India as an NRI comes with a few extra regulations. By using the right account type, sticking to delivery-based trades, and seeking help or a reliable broker, you can enjoy the benefits of the vibrant stock market of India.
Further, if you need more information about NRI investment plans, connect with Savetaxs. We are a team of financial experts who help you choose the best investment as per your financial goals, risk appetite, and time horizon. Additionally, we can also help you with your tax planning in India.
Note: This guide is for information purposes only. The views expressed in this guide are personal and do not constitute the views of Savetaxs. Savetaxs or the author will not be responsible for any direct or indirect loss incurred by the reader for taking any decision based on the information or the contents. It is advisable to consult either a CA, CS, CPA or a professional tax expert from the Savetaxs team, as they are familiar with the current regulations and help you make accurate decisions and maintain accuracy throughout the whole process.

Mr. Ritesh has 20 years of experience in taxation, accounting, business planning, organizational structuring, international trade financing, acquisitions, legal and secretarial services, MIS development, and a host of other areas. Mr Jain is a powerhouse of all things taxation.
- NRI Purchasing Property In India From The USA - A Complete Guide
- Normal Demat Account Vs NRI Demat Account - Key Differences
- Difference Between Repatriable Vs. Non-Repatriable Investments for NRIs
- Everything You Need to Know About Hybrid Mutual Funds for NRIs
- Should NRIs Link their DEMAT Account to an NRE or NRO Account?
- Why Is Licence Agreemnt Better Than Rent Agreement For NRIs
- Monthly Income Investments for NRIs in India
- How NRIs Can Retire Early Using the FIRE Strategy?
- Your Detailed Guide for Gift City Funds for NRIs
- Step-by-Step Guide to NRI Investment in Mutual Funds
- What Are the Trading Restrictions for NRIs?
- Financial Planning for NRIs in Singapore: What to Consider?
- Mutual Funds vs Real Estate: Best Investment Options for NRIs
- Financial Planning For NRIs In The USA - Manage Your Money Wisely
- Why NRIs Must Invest in Child Plans in India for Best Returns?
Want to read more? Explore Blogs
Frequently Asked Questions
No matter what your source of income is, we've got you covered. There’s a plan for everybody!
_1767955810.png)
_1767164087.webp)











-DEDUCTION-ON-HOSUING-LOAN_1756903528.webp)
